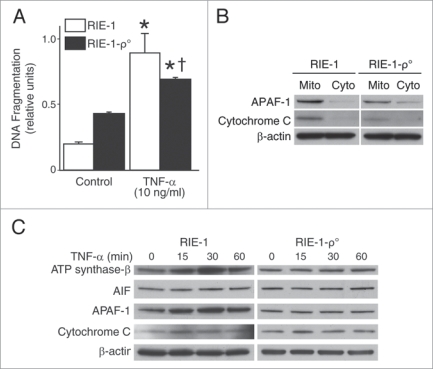
Figure 3.
TNFα activates mitochondrial apoptotic pathways and induces significant intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. (A) RIE-1 and RIE-1-ρ° cells were treated with TNFα as before. apoptosis was measured by DNA fragmentation ELISA. Data represent triplicate determinations (mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05 vs. control; †p < 0.05 vs. TNFα-treated RIE-1 cells) and experiments were repeated 3 times. TNFα-induced apoptosis was attenuated when compared to RIE-1 cells. (B) RIE-1 and RIE-1-ρ° cells (2 × 107) were plated for 24 h, mitochondria isolated for protein analysis of mitochondrial apoptotic markers, cytochrome c and APAF-1, by western blotting. Mitochondrial DNA-damaged RIe-1-ρ° cells showed attenuated mitochondrial protein levels. (C) TNFα treatment resulted in increased expression of mitochondrial apoptotic markers (AIF, APAF-1, cytochrome c and ATP synthase-β) in RIE-1 cells by western blotting. Mitochondrial DNA-damaged RIe-1-ρ° cells treated with TNFα showed unchanged basal levels of all apoptotic markers except for increased expression of cytochrome c at 15 min.