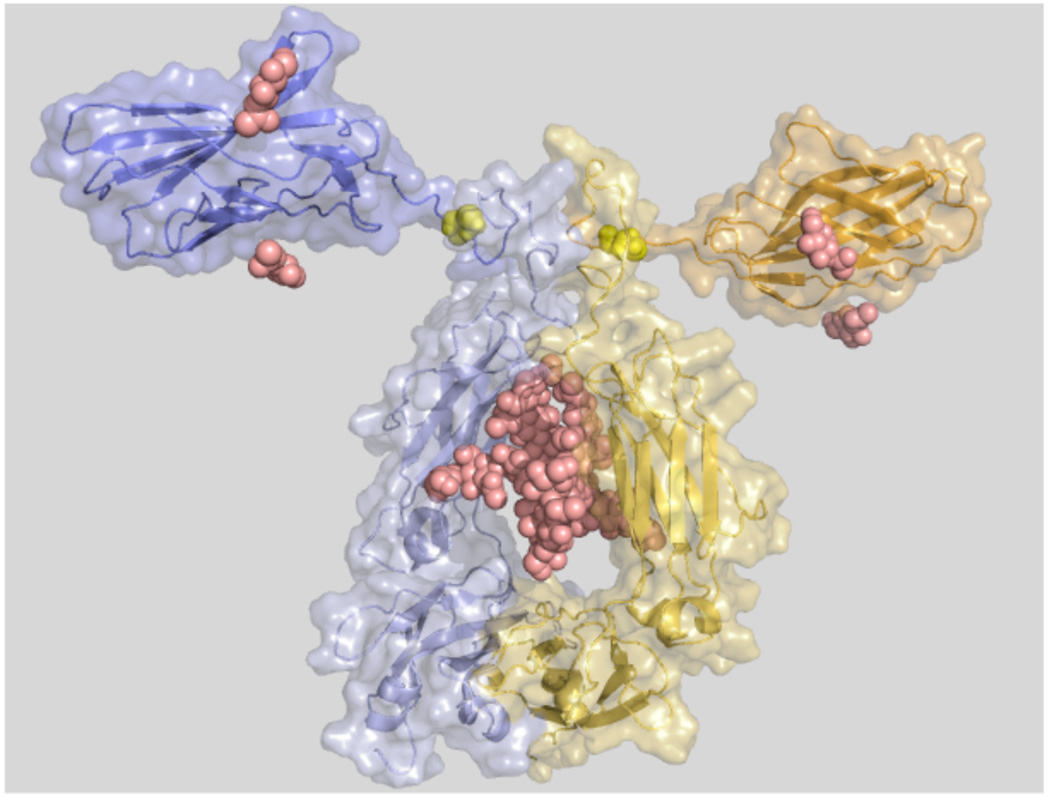
Figure 2.
Structural model of abatacept. Blue and yellow cartoon and surface representations for each chain. Small domains (top) are the extracellular soluble domains of human CTLA-4. Large domains are the CH2 and CH3 domains in the modified Fc part of human IgG1. Yellow spheres are Cys120 in CTLA-4 that makes a disulphide connection between the chains. Sugar residues are represented as pink spheres. The amino acid sequence of one chain of abatacept was sent to the Robetta server (http://robetta.bakerlab.org/) for structure prediction. Robetta models were aligned in PyMOL (http://pymol.org/) with the heavy chains of IgG1 from 1HZH to build a dimer. To create the final dimer model, the CTLA-4 domain predicted by Robetta was replaced by the actual crystal structure of CTLA-4 (PDB id 1I8L) by aligning the crystal structure with each of the modeled domains in the dimer model. Graphics were made in PyMOL.