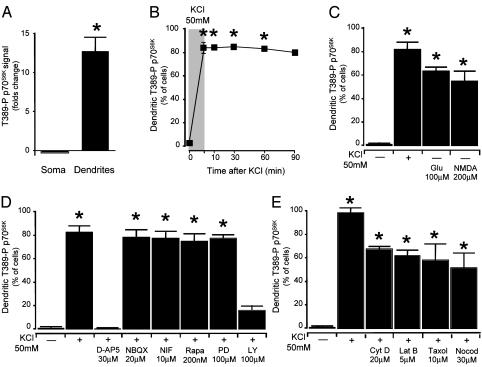
Fig. 6.
Dendritic activation of Thr-389-P p70S6K is NMDA- and PI3K-dependent. (A) Quantification of immunoreactivity for Thr-389-P p70S6K in primary hippocampal neurons after depolarization with KCl (50 mM), as shown in Fig. 5. The intensity of Thr-389-P p70S6K immunoreactivity was greatly increased in dendrites after depolarization with KCl, whereas it was not significantly reduced in the somata. (B) Thr-389-P p70S6K was persistently activated in the dendrites after withdrawal of KCl. (C) Dendritic accumulation of Thr-389-P p70S6K could also be induced by application of glutamate or NMDA. (D) Accumulation of Thr-389-P p70S6K in dendrites was sensitive to the NMDA antagonist D-AP5 and the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (NIF, nifedipine; Rapa, rapamycin; PD, PD98059; LY, LY294002). (E) Dendritic activation of Thr-389-P p70S6K was not prevented either by the actin polymerization inhibitors cytochalasin D and Latrunculin B or by the inhibitors of microtubule polymerization taxol and nocodazole (*, P < 0.01 from control).