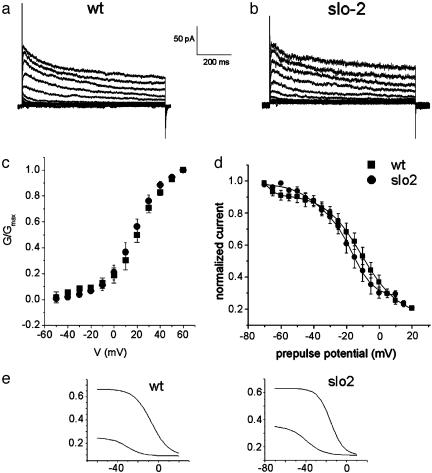
Fig. 1.
The voltage-dependent outward component in WT and slo-2 mutant cells. Comparison of whole-cell currents from a WT cell in low Ca2+, low Cl- intracellular concentrations (10 nM and 4 mM, respectively) (a) and a slo-2 mutant cell (b). Currents were elicited from a -70 mV holding potential, in 10-mV steps from -70 to +60 mV. (c) G-V data plotted for WT cells (▪; n = 5), in low intracellular Ca2+/Cl- solution; and slo-2 mutant cells (•; n = 7). G-V data were plotted as described in Materials and Methods, using a value of -70 mV for K+ reversal potential (Ek), which is close to the expected K+ equilibrium potential of ≈-80 mV. (d) Prepulse inactivation data for WT cells (▪, n = 6) and slo-2 mutants (•, n = 5). Curves were obtained as described in Materials and Methods and fitted with the sum of two Boltzmann functions (1 and 2). (e) Each of the two components was plotted separately for both WT and slo-2 cells. The parameter values for each component were comparable between WT and slo-2 cells, respectively: V0.5(1) = -6.9 mV, k(1) = 8.5; V0.5(2) = -30.9 mV, k(2) = 7.6 and V0.5(1) = -15.6, k(1) = 6.33; V0.5(2) = -39.3 mV, k(2) = 8.4.