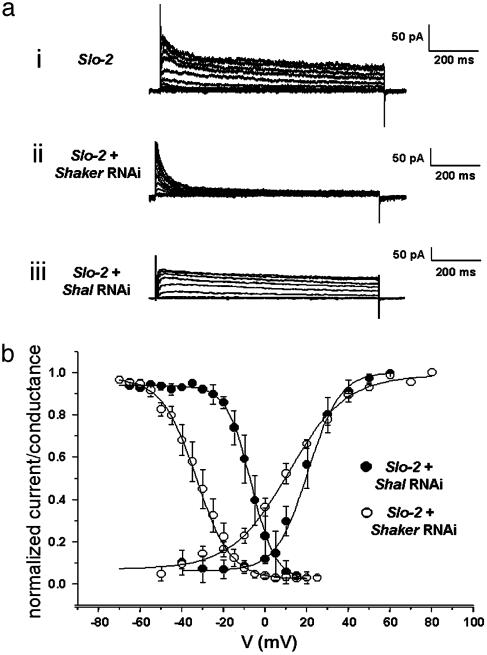
Fig. 2.
Dissection of voltage-dependent components by RNAi. The slo-2 mutant was used to obtain these data so that there would be no chance of contamination from the SLO-2 current. (ai) Family of K+ currents obtained from a slo-2 mutant muscle cell showing only the voltage-dependent components. (aii) Family of K+ current traces for SHAL currents (slo-2 mutant cell treated with Shaker RNAi). (aiii) SHAKER currents (a slo-2 mutant cell treated with Shal RNAi). Cells were held at -70 mV and stepped from -70 to +60 mV in 10-mV increments. (b) G-V plots and prepulse inactivation curves for SHAL currents (○) and SHAKER currents (•). The activation parameter values were V0.5a = 11.2 ± 1.5 mV, ka = 14.1 ± 1.04 (n = 5); V0.5a = 20.4 ± 2, ka = 7.7 ± 1.1 (n = 3) for SHAL and SHAKER currents, respectively. SHAL currents inactivated with values of V0.5i =-33.1 mV ± 1.2 and ki = 8.3 ± 0.7 (n = 6), whereas SHAKER inactivation parameter values were V0.5i =-6.95 ± 1.7, ki = 5.8 ± 0.5 (n = 2). Internal concentrations of Cl- and Ca2+ were, respectively, 120 mM and 10 nM.