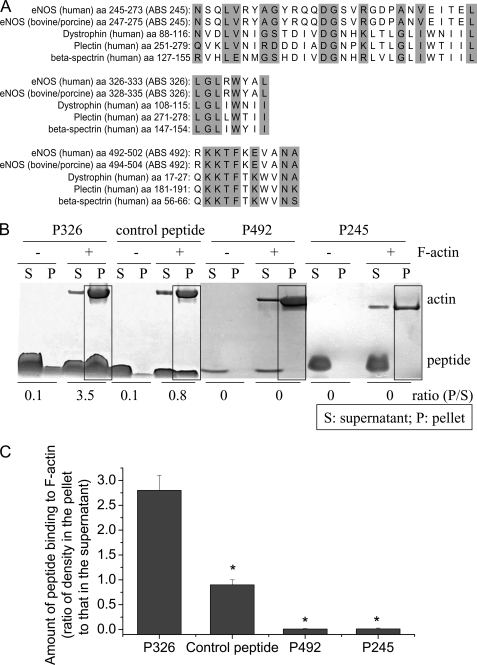
FIGURE 2.
Panel A, alignment of the sequences of the three putative ABSs to actin-binding proteins. Three regions in the eNOS oxygenase domain were found to have high consensus with ABS on actin-binding proteins. The highlight indicates same or similar amino acids. Panel B, ABS peptide 326 specifically binds to β-actin. ABS peptides 326 (P326), control peptide, ABS peptides 492 (P492), and ABS peptides 245 (P245) at final concentrations of 10 μm were incubated alone or with 23 μm F-actin in F-actin buffer for 30 min. After high speed centrifugation at 150,000 × g for 2 h, the supernatants and pellets were subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis. The boxes show co-sedimentation of peptides with F-actin in the pellets. The image shown is representative of three experiments. Panel C is a bar graph depicting the changes in the amount of peptide binding to F-actin expressed as the ratio of peptide density in the pellet to that in the supernatant. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.; n = 3 experiments. *, p < 0.05 versus P326.