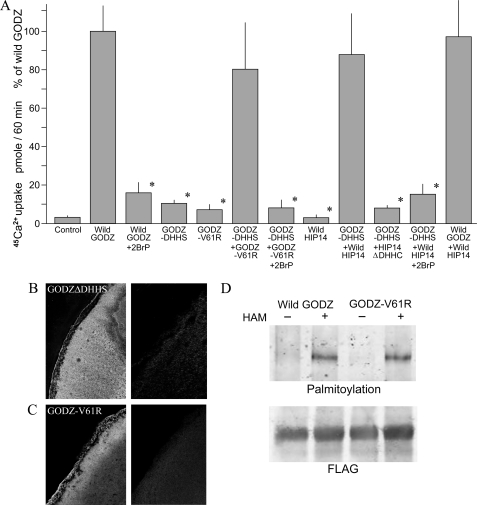
FIGURE 2.
Palmitoyl acyltransferase modulates GODZ-mediated Ca2+ transport. Where indicated, oocytes were injected with wild-type GODZ, GODZ-DHHS, mutant GODZ-V61R, wild-type HIP14, or HIP14ΔDHHC cRNA. Also where indicated, expressing oocytes were treated with and without 75 μm 2-bromopalmitate (2BrP) for 3 h prior to experimentation. A, summary of 45Ca2+ uptake rates. The methods used were those described in the legend to Fig. 1B. The results were normalized to wild-type GODZ and are represented as means ± S.E. for n > 12 oocytes. *, p < 0.01, from determinations with wild-type GODZ-expressing oocytes. B, left panel, surface expression of GODZ-DHHS mutant protein in cRNA-injected X. laevis oocytes as determined by immunofluorescence; right panel, absence of GODZ-DHHS expression in water-injected oocytes. C, left panel, surface expression of GODZ-V61R protein in oocytes as determined by immunofluorescence; right panel, absence of GODZ-V61R expression in water-injected oocytes. D, mutant GODZ-V61R retains the palmitoyl acyltransferase function as indicated by biotin-BMCC bands in the presence of hydroxylamine (HAM). Gels are representative of three independent experiments.