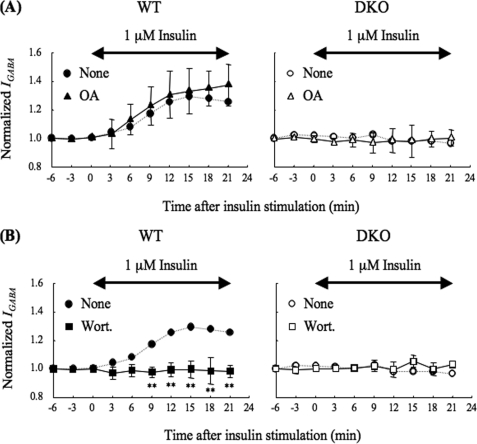
FIGURE 2.
Effect of okadaic acid or wortmannin on the insulin-potentiation of IGABA. A, effect of okadaic acid on the insulin potentiation of IGABA. Neurons from WT (left panel, closed triangles, n = 8) or DKO (right panel, open triangles, n = 3) mice were pretreated with 10 μm okadaic acid, an inhibitor of the protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A (42), for 15 min and throughout the experiment. The experiment was performed as shown in Fig. 1A except for the okadaic acid treatment. All data are represented as means ± S.D. The IGABA from WT (left panel, closed circles, dashed line) or DKO (right panel, open circles, dashed line) mice without okadaic acid (none), which were taken from Fig. 1A, are also shown as references. B, effect of wortmannin on the insulin potentiation of IGABA. Neurons from WT (left panel, closed squares, n = 6) or DKO (right panel, open squares, n = 3) mice were pretreated with 100 nm of wortmannin, a potent PI 3-kinase inhibitor (45), for 15 min and throughout the experiment. The experiments were performed as shown in Fig. 1A except for the wortmannin treatment. All data are represented as means ± S.D. The IGABA from WT (left panel, closed circles, dashed line) or DKO (right panel, open circles, dashed line) mice without wortmannin (none), which were taken from those shown in Fig. 1A, are also shown as references. Double-headed arrows indicate the period of insulin stimulation. Significance was determined using the Student's t test (**, p < 0.01 from the results obtained in the absence of the drug). none, no addition; OA, okadaic acid; Wort, wortmannin.