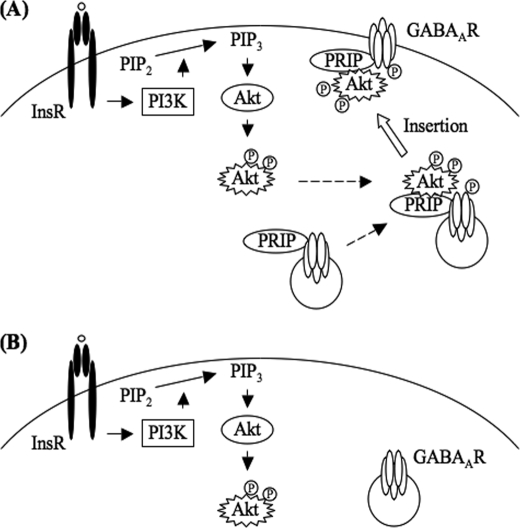
FIGURE 7.
Schematic representation of the role of PRIP in insulin-induced membrane insertion of GABAA receptors. A, insulin stimulation induces Akt activation in a PI 3-kinase-dependent manner. Subsequent phosphorylation of the β-subunits of GABAA receptors by Akt is facilitated by PRIP through the ternary complex formation with activated Akt and β-subunit, which triggers an enhancement of the insertion of GABAA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane. B, absence of PRIP fails in making activated Akt accessible to β-subunit. Arrows indicate the signaling pathways to activate downstream target. Dashed arrows indicate the complex formation. White arrow indicates membrane insertion of GABAA receptor. InsR, insulin receptor; GABAAR, GABAA receptor, PI3K, PI 3-kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, PRIP, PLC-related but catalytically inactive protein. Circled P indicates the phosphorylation.