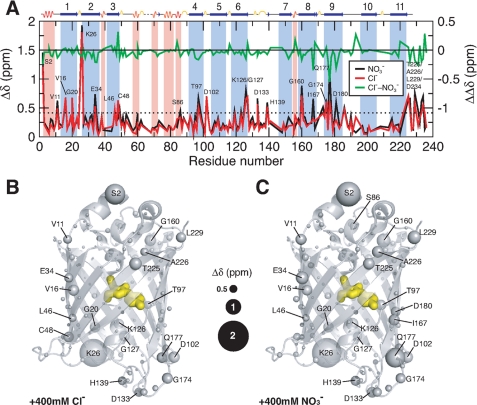
FIGURE 4.
Structural mapping of chemical shift perturbations in Venus upon addition of chloride and nitrate ions. A, chemical shift perturbations (Δδ) of Venus in the presence of 400 mm chloride (red) and nitrate ions (black) as a function of residue number. The weighted Δδ is defined as (Δδ(1H)2 + (0.65·Δδ(15N)2)1/2. The differences between chloride and nitrate ions (ΔΔδ) are shown in green with a shifted base line to illustrate the similar effects induced by the two different ions. The dashed horizontal line indicates the values of two standard deviations (2σ) of all Δδ. The residues that exhibit Δδ values larger than 2σ are indicated with corresponding residue identities. Residues that are located in the α-helical and β-stranded regions are shaded in pink an light blue, respectively, with the secondary structures shown on top of the panel. Structural mapping of the chemical shift perturbations induced by the addition of 400 mm chloride ions is shown in B and that induced by the addition of 400 mm nitrate ions is shown in C. The backbone nitrogen atoms are shown in spheres with various sizes proportional to the observed chemical shift perturbations (as indicated in the middle). The chromophore within the β-barrel is shown as yellow sticks.