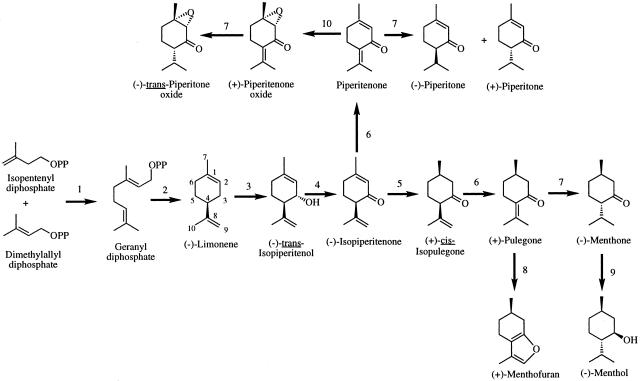
Fig. 1.
The principal pathways for monoterpene biosynthesis in peppermint. The responsible enzymes are as follows: geranyl diphosphate synthase (1); (-)-limonene synthase (2); cytochrome P450 (-)-limonene-3-hydroxylase (3); (-)-trans-isopiperitenol dehydrogenase (4); (-)-isopiperitenone reductase (5); (+)-cis-isopulegone isomerase (6); (+)-PR (7); cytochrome P450 (+)-MFS (8); (-)-menthone reductase (9); and the terpenoid epoxidase (10). OPP denotes the diphosphate moiety.