Figure 1.
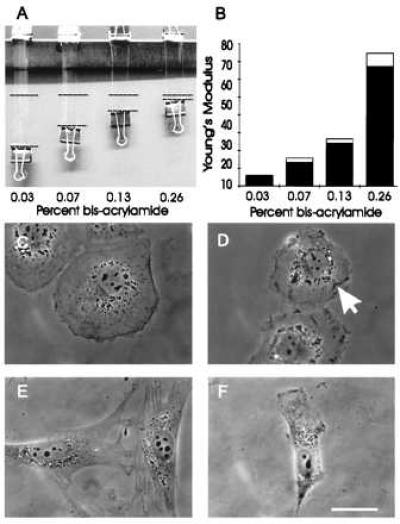
Mechanical characteristics of polyacrylamide substrates and effects on cell morphology. (A and B) identically sized strips of polyacrylamide with various acrylamide/bis-acrylamide ratios were fixed at one end and stretched at the other end with a downward force of 0.103 N. The dashed lines represent the amount of stretching caused by applied weight (A). The extent of stretching was then used for the calculation of Young’s modulus, expressed as N/m2 (B). (C–F) Phase morphology of NRK (C and D) or 3T3 (E and F) cells plated on substrates containing 0.26% bis- (C and E) or 0.03% bis-acrylamide (D and F). NRK cells on the more flexible substrate are less well spread and contain irregular ruffles on the ventral surface (D, arrow), as determined by optical sectioning at a high magnification. Similarly, 3T3 cells on the substrate of high flexibility are typically less well spread and with a polarized morphology (F). Bar = 10 μm.
