Figure 3.
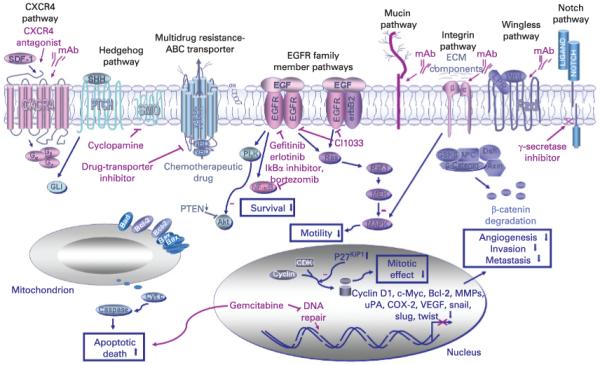
Scheme showing the novel therapeutic strategies against locally advanced and/or metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAs) by targeting different oncogenic cascades signalling elements in pancreatic cancer cells. The cytotoxic agents acting as the potent inhibitors of the tumorigenic cascades including the selective inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor–epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF–EGFR) system (gefitinib, erlotinib and CI1033), smoothened hedgehog signalling element (cyclopamine), Notch (γ-secretase inhibitor), ATP-binding cassette (ABC) multidrug transporter inhibitor, CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) antagonist and monoclonal antibody (mAb) directed against CXCR4, mucin, integrin or Wnt ligand are also indicated. Moreover, growth inhibitory and apoptotic effects induced by the current chemotherapeutic drug, gemcitabine, are illustrated. CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; Cyt c, cytochrome c, Fzd, frizzled receptor; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MEK, extracellular signal-related kinase kinase; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; NBD, nucleotide binding domain; SMO, smoothened; uPA, urokinase plasminogen activator; VEGF, vascular epidermal growth factor; Wnt, wingless ligand.
