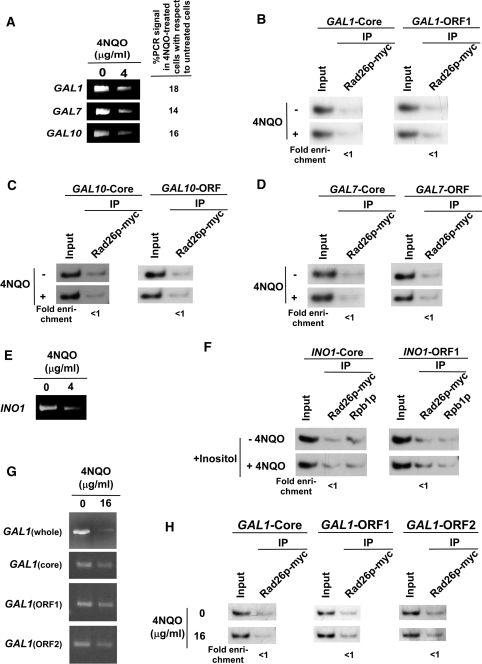
Figure 3.
The DNA lesion alone does not target the recruitment of Rad26p in the absence of active transcription. (A) Analysis of DNA damage at the GAL1, GAL7 and GAL10 loci within the first 20 min of 4NQO treatment. The yeast cells were grown in YPR, and then treated with 4NQO for 20 min. The genomic DNA was prepared and was analyzed by PCR. (B) The DNA lesions at the GAL1 gene do not target the recruitment of Rad26p in the absence of active transcription. The yeast strain carrying myc-tagged Rad26p was grown in YPR up to an OD600 of 1.0, and then treated with 4NQO for 20 min prior to cross-linking. The ChIP assay was carried out as in Figure 1A. The fold change of Rad26p ChIP signal at GAL1 in 4NQO-treated cells in comparison to untreated cells under transcriptionally inactive conditions. The DNA lesions at the GAL10 (C) and GAL7 (D) genes also do not target the recruitment of Rad26p in the absence of active transcription. (E) Analysis of DNA damage at the INO1 gene within the first 20 min of 4NQO treatment. Yeast cells were grown in synthetic complete medium containing 100 µM inositol at 30°C up to an OD600 of 1.0, and then treated with 4NQO for 20 min. The whole INO1 gene was amplified by PCR, using the specific primer pairs as mentioned in Table 1. (F) The DNA lesions at the INO1 gene do not target the recruitment of Rad26p in the absence of active transcription. The yeast strain expressing myc-tagged Rad26p was grown in the synthetic complete medium containing 100 µM inositol at 30°C up to an OD600 of 1.0, and then treated with 4NQO for 20 min prior to cross-linking. (G) Analysis of DNA damage at the GAL1 locus within the first 10 min of 4NQO treatment at a concentration of 16 µg/ml. The yeast cells were grown in YPR and treated with 4NQO as in (A). The whole GAL1 locus, core promoter, ORF1 and ORF2 regions were amplified by PCR, using the specific primer pairs as mentioned in Table 1. (H) Analysis of the association of Rad26p with GAL1 following 4NQO treatment at the concentration of 16 µg/ml in the absence of transcription. Yeast cells were grown in YPR. The ChIP assay was performed as in Figure 1A. The fold change of Rad26p ChIP signal at GAL1 in 4NQO-treated cells in comparison to untreated cells under transcriptionally inactive conditions.