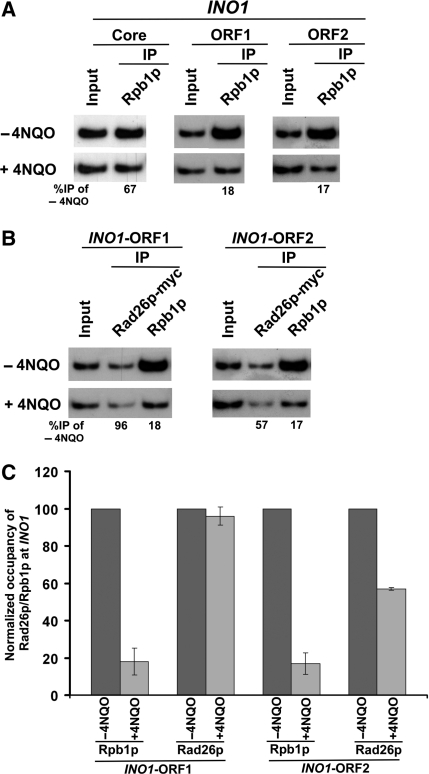
Figure 6.
RNA polymerase II promotes the recruitment of Rad26p to the site of DNA lesion at the coding sequence of the active INO1 gene. (A) Analysis of association of RNA polymerase II with the INO1 coding sequence in the presence and absence of 4NQO-induced DNA damage. The INO1 gene was induced prior to 4NQO treatment (4 µg/ml) for 20 min as described in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section. As a control, yeast cells were also grown under similar growth conditions without 4NQO treatment. These cells were used for the ChIP assay to analyze the level of Rpb1p at the INO1 ORF in 4NQO-treated (+) and untreated (−) cells. (B) Analysis of the recruitment of Rad26p towards the 5′- and 3′-ends (ORF1 and ORF2, respectively) of the INO1 ORF in the presence and absence of the 4NQO-induced DNA damage. The yeast strain carrying myc-tagged Rad26p was grown and cross-linked as in (A). Immunoprecipitation was performed as in Figure 1A. (C) The data of the (A and B) were plotted in the form of a histogram.