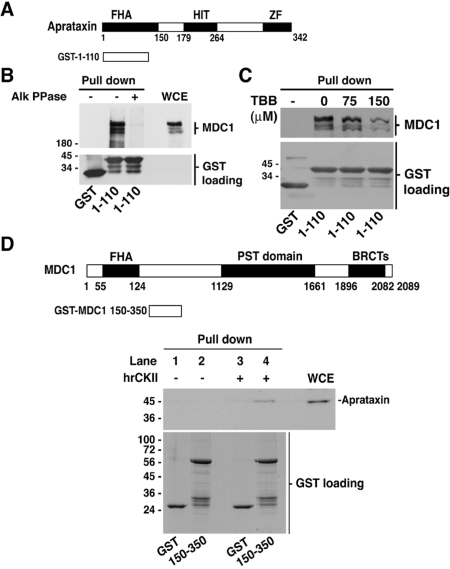
Figure 3.
CK2-mediated phosphorylation-dependent binding of MDC1 to the aprataxin FHA domain. (A) Diagram of aprataxin GST fusion used in the pull-down assays. (B) Effect of protein phosphatase activity on MDC1 binding to the aprataxin FHA domain. Whole cell extracts from HeLa cells were mock treated or treated with alkaline phosphatase (Alk PPase: 2500 U) for 1 h at room temperature and subsequently used for pull-down assays using GST only, and GST-aprataxin FHA domain. (C) Reduced binding of MDC1 to the aprataxin FHA domain following CK2 inhibitor treatment. HeLa cells were treated for 8 h with increasing concentrations of CK2 inhibitor TBB, lysed and WCE were used for GST pull-down assays. (D) Schematic of MDC1 protein sequence showing the GST fusion protein (150–350) used in the pull-down assays. In vitro binding of CK2-phosphorylated (150–350) region of MDC1 with HeLa WCE. Binding endogenous aprataxin to CK2-phosphorylated MDC1 (150–350) fragment was revealed by immunoblotting.