Figure 5.
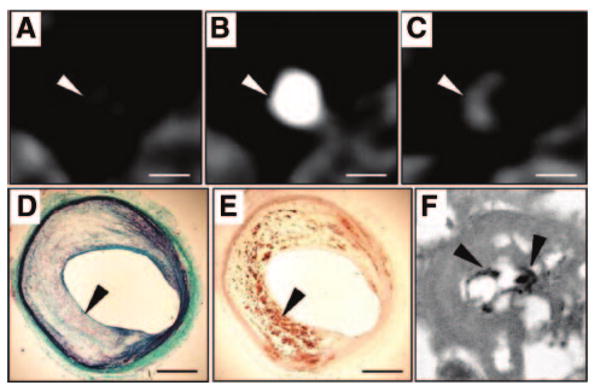
Detection of macrophages with N1177-enhanced CT. CT axial views of an atherosclerotic plaque in a rabbit aorta before (A), during (B), and 2 hours after (C) the intravenous injection of the contrast agent N1177. Note the strong enhancement of the aortic wall detected with CT 2 hours after the injection of N1177 (C; white arrowhead). On axial sections corresponding to the CT images, atherosclerotic plaque was characterized by a large lipid-rich core covered by a thin cap of collagen stained in green with Masson trichrome (D; black arrowhead) and intense macrophage infiltration in the lipid-rich core detected by immunohistochemistry for macrophages with a monoclonal RAM-11 antibody (E; black arrowhead). Numerous iodine particles (black arrowheads) were detected with transmission electron microscopy, next to lipid inclusions, in lysosomes of macrophages from atherosclerotic plaques (F). White scale bar, 5 mm; black scale bar, 1 mm. Adapted from Hyafil et al.92
