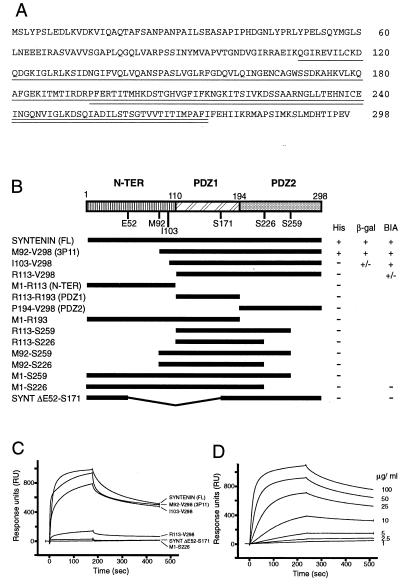
Figure 1.
Structure of syntenin and domains of syntenin necessary for the interaction with syndecans. (A) Amino acid sequence of syntenin. The two PDZ domains are indicated by the single and double underlinings. (B) Different parts of the original clone (3p11) and of the syntenin cDNA were subcloned in the pGAD10 vector or the pGEX vector to code for fusions between the activating domain of Gal4 (Gal4 AD) or GST and various full-length, truncated, and deleted versions of syntenin. Interactions between syntenin and the syndecan-2 cytoplasmic domain were scored in the yeast two-hybrid system as growth on His− plates and β-galactosidase activity. (C) Binding of GST–syntenin fusion proteins to a streptavidin-immobilized biotinylated synthetic peptide that represents the 32 cytoplasmic amino acids of syndecan-2, as detected by surface plasmon resonance. (D) Binding curves obtained at different concentrations of the GST full-length syntenin fusion protein.