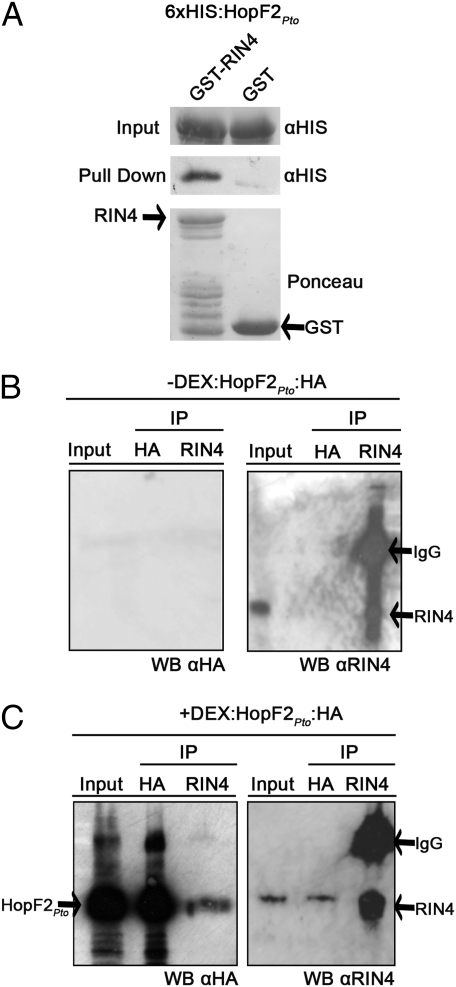
Fig. 3.
HopF2Pto interacts with RIN4 both in vitro and in vivo. (A) GST:RIN4- or GST-bound glutathione resin was incubated with recombinant 6xHIS:HopF2Pto, washed and probed for the presence of bound 6xHIS:HopF2Pto (see Methods). Equal volumes of 6xHIS:HopF2Pto added to GST:RIN4- or GST-bound glutathione resin were immunoblotted and probed with HIS antisera before washes (Top) or following washes (Middle). (Bottom) Ponceau stain before washes as a loading control. The GST and full-length RIN4 bands are indicated by an arrow. Bands below the full-length RIN4 band are RIN4 degradation products as determined by an anti-RIN4 blot (Fig. S9). (B and C) HopF2Pto associates with RIN4 in vivo. (B) Uninduced HopF2Pto transgenic leaves were harvested 24 h after mock treatment. Ten micrograms of input protein (Input) or entire elution (50 μL) of the immunoprecipitation (IP) by α-HA or α-RIN4 was loaded onto the SDS/PAGE gel and probed with the indicated antisera (see Methods). (C) HopF2Pto transgenic leaves were harvested 24 h after 30 μM DEX application and treated as described in B. α-HA immunoblot detects the presence of HopF2Pto:HA.