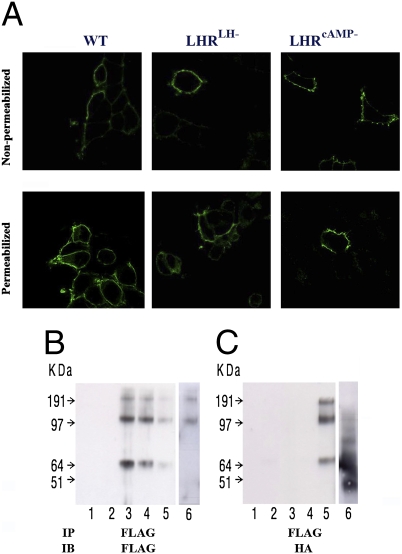
Fig. 2.
LHR cellular localization and di/oligomerization. (A) Cell surface expression. HEK-293 cells expressing tagged-LHRs (HA-WT, HA-LHRLH−, or FLAG-LHRcAMP−) were immunostained using anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibodies, respectively, and secondary antibodies labeled with fluorescent dyes, and analyzed by confocal microscopy. All three receptors (WT and mutants) could be detected on the cell surface as shown on nonpermeabilized cells (Upper), while some receptor immunoreactivity was detected in the ER of permeabilized cells (Lower). This proves that the WT and mutant receptors are transported to the cell surface. (B and C) Dimerization/oligomerization of mutant mLHRs. HEK-293 cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged signaling-deficient (FLAG-LHRcAMP−) and HA-tagged binding-deficient (HA-LHRLH−) mutant constructs. Lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody. Thereafter, the immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS/PAGE under reducing conditions, and immunoblots (IB) were probed with either anti-FLAG antibody (B) or anti-HA antibody (C). Both monomeric and higher molecular weight LHR complexes were detected. These data indicate that FLAG-LHRcAMP− mutant interacts with HA-LHRLH− mutant. The lanes are: 1, control vector (pcDNA); 2, HA-LHRLH−; 3, FLAG-LHR−cAMP; 4, combined lysates from separately FLAG-LHR−cAMP and HA-LHR−LH transfected cells; 5, coexpressed FLAG-LHR−cAMP + HA-LHR−LH; 6, coexpressed FLAG-LHRcAMP− + HA-β2-AR (different experiment with identical conditions).