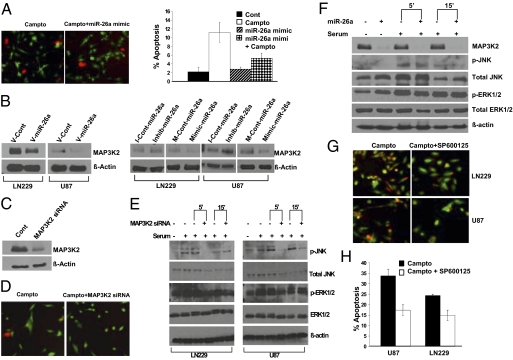
Fig. 4.
miR-26a decreases MAP3K2/MEKK2 expression and inhibits JNK-dependent apoptosis. (A) (Left) Live cell (green)/dead cell (red) assay for U87 GBM cells after exposure to camptothecin (50 μM) overnight. U87 cells were treated with the miR-26a mimic or a control oligonucleotide (200 nM) before exposure to camptothecin. (Right) Quantification of the data shown to the Left. Mean ± SEM is shown (P = 0.05, t test). (B) (Left) MAP3K2/MEKK2 protein expression in LN229 and U87 GBM cells transduced with a miR-26a virus (V-miR-26a) or a control virus (V-Cont). (Right) Effect of miR-26a mimic or inhibitor (200 nM) on MAP3K2/MEKK2 protein expression in U87 and LN229 cells. (C) Effect of MAP3K2 siRNA on MAP3K2/MEKK2 protein expression in 293T cells. (D) Live cell (green)/dead cell (red) assay for U87 cells transfected with MAP3K2/MEKK2 siRNA or a control oligonucleotide before exposure to camptothecin. (E) Effect of MAP3K2 siRNA on serum-stimulated JNK phosphorylation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in LN229 and U87 cells. Protein isolates were collected at 0, 5, and 15 min after the addition of serum. Of note, serum alone induced a decrease in total JNK expression over time. (F) Effect of miR-26a mimic (200 nM) on MAP3K2/MEKK2 expression, serum-stimulated JNK phosphorylation, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in LN229 GBM cells. (G) Live cell (green)/dead cell (red) assay for U87 and LN229 cells treated with the specific JNK inhibitor SP600125 (50 μM) or an inactive control compound before exposure to camptothecin overnight. (H) Quantification of data shown in G. Mean ± SEM is shown (P = 0.0041 and P = 0.013 for U87 and LN229 cells, respectively, t test).