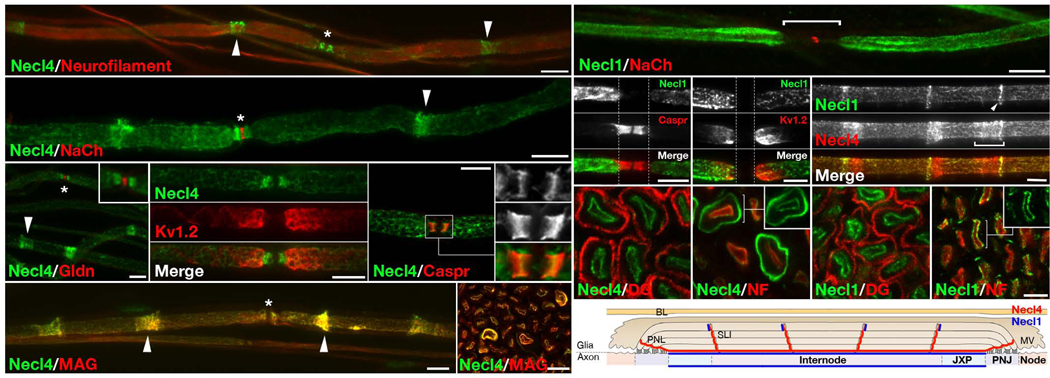
Figure 3. Necl4 and Necl1 are localized along the internodes.
(a–f) Immunofluorescence staining of teased adult rat sciatic nerves for Necl4 and (a) Neurofilament, (b) Na+ channels (NaCh; to label nodes), (c) Gliomedin (Gldn; to label nodes), (d) Kv1.2 (to label juxtaparanodes), (e) Caspr (to label paranodes), or (f) myelin–associated glycoprotein (MAG), as indicated. (g) Cross sections of adult rat sciatic nerves labeled for Necl4 and MAG. Arrowheads and asterisks mark the incisures and the nodes of Ranvier, respectively. Inset in c shows a higher magnification of the nodal region. Insets in e show a higher magnification of the paranodes labeled for Necl4 (upper), Caspr (middle) or the merged image (lower). (h–k) Teased fibers immunolabeled for Necl1 and (h) Na+ channels, (i) Caspr, (j) Kv1.2 or (k) Necl4 as indicated. The location of the nodes and paranodes is marked with a horizontal line in h, or with dashed vertical lines in i–j. Note that Necl1 is present along the axonal internodes but is absent from the paranodes or the nodes of Ranvier. The Schmidt–Lanterman incisures, or their outermost ring (arrowhead) is labeled in k. (g–j) Cross sections of adult rat sciatic nerves labeled for Necl4 (l–m) or Necl1 (n–o), together with neurofilament (NF) or dystroglycan (DG), as indicated. (p) A schematic view of a longitudinal section of a myelinated axon, summarizing the localization of Necl4 and Necl1. PNL–Paranodal loops; PNJ– Paranodal junction; JXP–Juxtaparanodal region; SLI–Schmidt– Lanterman incisures; MV–Microvilli; BL–basal lamina. Scale bar: (a–k) 10 µm; (i– o) 5 µm.