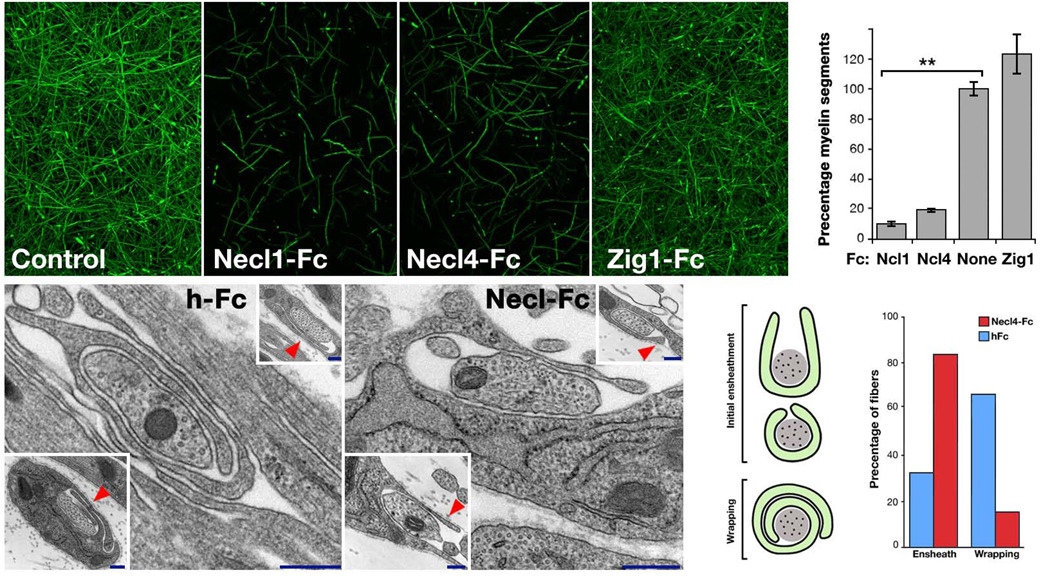
Figure 6. Necl–mediated axon–glia interaction is required for myelination.
Myelinated DRG–cultures were left untreated (a), or grown in the presence of Fc– fusion proteins (50 µg ml−1) containing the extracellular domain of Necl1 (Necl1–Fc; b), Necl4 (Necl4–Fc; c) or Zig1 (Zig1–Fc; d) for 10 days, and then immunostained for MBP. The number of MBP–positive segments present in each condition is shown as a percentage of that in the untreated cultures (e). Cultures grown in the presence of Necl–Fc’s contained significantly (**p<0.005) fewer myelin segments compared to untreated or control–treated (Zig1–Fc) cultures. (f–i) Electron microscopy analysis of myelinating cultures. (f–g) Representative images of 9–day–old DRG and Schwann cells cultures, grown in the presence of human Fc (f) or Necl4–Fc (g). Two additional examples are shown in the insets. Note that while in the control Fc–treated cultures Schwann cell processes already circled 1.5 times around the axon, they fail to do so when the cultures were grown in the presence of Necl4–Fc (red arrowheads). (h) Schematic representation of axons ensheathed (U shape and O shape) and wrapped (1.5 turns and more) by myelinating Schwann cells. (i) The number of ensheathed and wrapped axons in each culture are shown as a percentage of the total sites counted (hFc n=87; Necl4–Fc n=118). Scale bar: a–d, 100 µm; g–h, 20 nm.