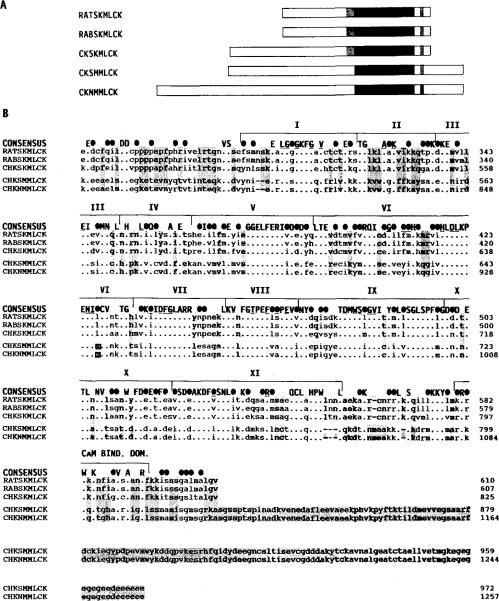
Fig. 3. Comparison of the primary structures of MLCKs from different tissues and species.
Panel A, a linear schematic shows full-length MLCKs (amino-terminal to carboxyl-terminal) from rat skeletal muscle (RATSKMLCK; Roush et al., 1988), rabbit skeletal muscle (RABSKMLCK; Takio et al., 1986), chicken skeletal muscle, chicken smooth muscle (CHKSMMLCK; Olson et al., 1990), and chicken fibroblasts (CHKNMMLCK; Shoemaker et al., 1990). The solid block indicates the position of the conserved catalytic cores. The shaded region amino-terminal of the catalytic cores of the skeletal muscle enzymes indicates a region of extended homology among these MLCKs. The shqded region carboxyl-terminal of the catalytic core indicates the position of the calmodulin binding domains. Panel B, amino acid sequence alignment of the same MLCKs is shown beginning with the region that is conserved amino-terminal of the catalytic core. A consensus sequence is shown above the sequence alignment. Within the consensus sequence, identical residues are indicated by capital letters and conservative substitutions by solid ovals. Conservation is based on the following groupings of structurally similar amino acids: basic polar R groups (K, R, and H); acidic and uncharged polar R groups (D, E, N, and Q); nonpolar chain R groups (M, L, I, and V); aromatic or ring-containing R groups (F, Y, W, and H); and small R groups with near neutral polarity (A, C, G, S, T, and P). Subdomains I-XI of the catalytic core (Hanks et al., 1988) and the calmodulin binding domain are bracketed above the consensus sequence. Residues that are conserved among all protein kinases are underlined in the consensus sequence. The GXGXXG consensus sequence found among nucleotide-binding proteins is within subdomain I. Subdomain II contains an invariant lysine among all protein kinases. Residues that are identical among all the skeletal muscle enzymes and different from the smooth and non-muscle enzyme are shaded, including the carboxyl-terminal extension of the smooth and non-muscle enzymes which are uniformly absent in the skeletal muscle enzymes.