Fig. 8.
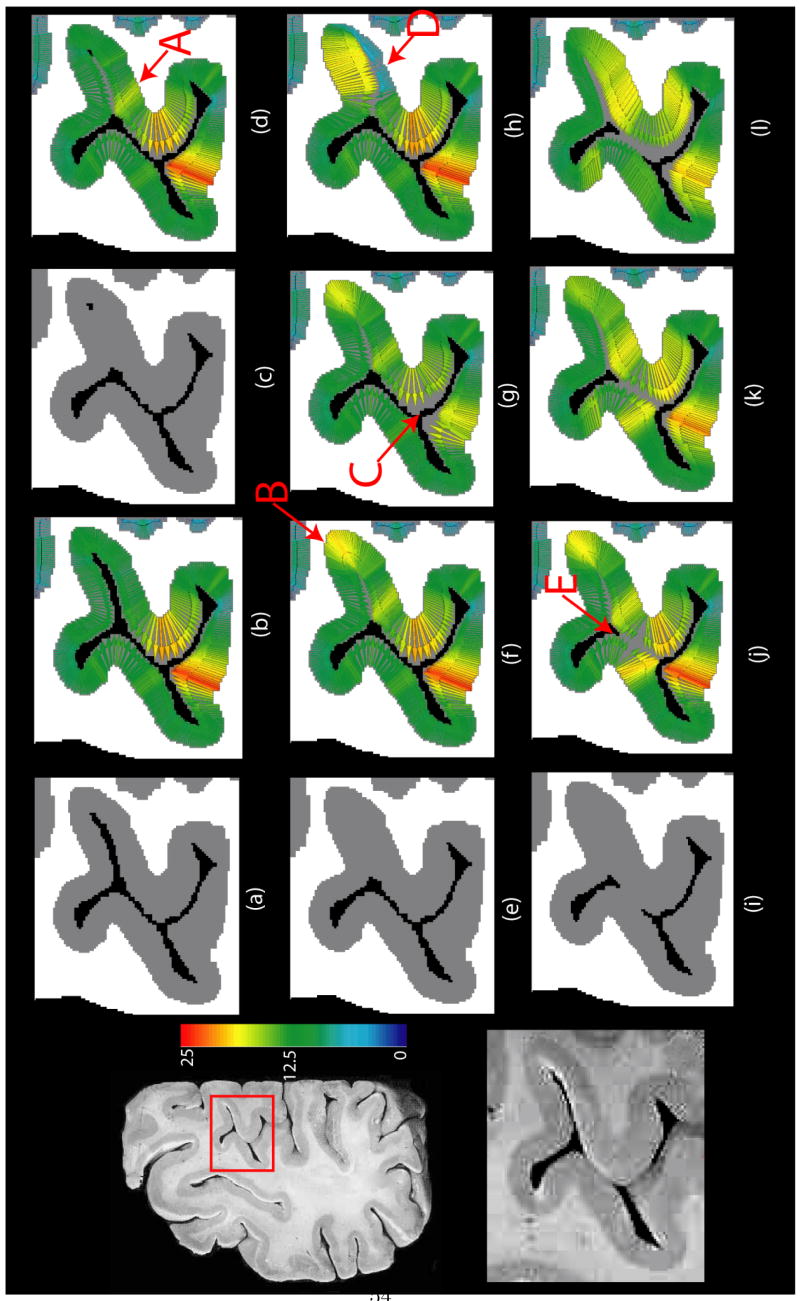
Results of running the proposed algorithm on a 2D high resolution brain slice. Left column: original slice (top) and the zoomed in section of cortex in inset (bottom). (a) Segmentation of the portion of the cortex in inset with all sulci resolved. (b) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (a). (c) Segmentation with only a few pixels of CSF resolved in the fundus. (d) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (c). (e) Segmentation with closed sulcus. (f) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (e) with a high prior making measurements unconstrained. (g) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (e) with a prior = 18. (h) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (e) with spatially varying prior, with a prior 6 on the lower bank of the closed sulcus and unconstrained elsewhere as in (f). (i) Segmentation with closed sulcus as in (e) and gyri touching each other in the middle. (j) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (i) with σ ≈ one voxel length. (k) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (i) with σ double that of (j). (l) DiReCT correspondence from segmentation in (i) with σ double that of (k). All quantities are measured in voxel units. See text for discussion.
