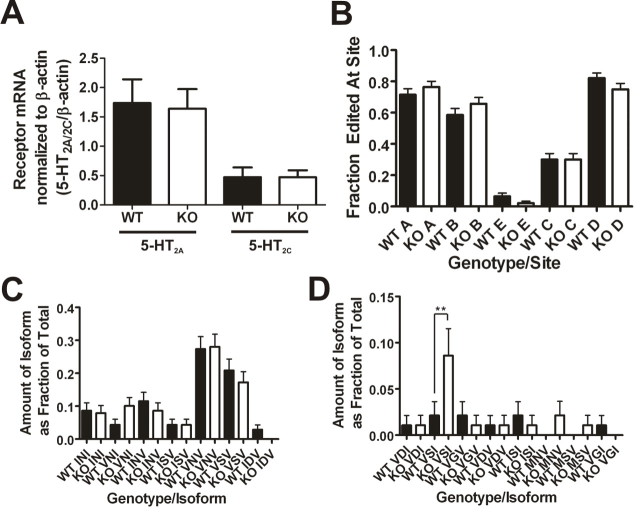
Figure 2.
Genetic deletion of PSD-95 does not affect mRNA levels of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors or mRNA editing of the 5-HT2C receptor. A, Cortical 5-HT2A receptor mRNA levels (N = 4 littermate pairs; 11 measurements were performed for each animal) and hippocampal 5-HT2C receptor mRNA levels (N = 4 littermate pairs; 5 measurements for each animal) normalized to β-actin mRNA levels as measured by quantitative RT-PCR. There are no changes in 5-HT2A mRNA levels and no changes in 5-HT2C mRNA levels in the absence of PSD-95. B, 5-HT2C mRNA editing frequencies at five edited sites. The frequency of editing at the five sites is not significantly different in PSD-95null mice. C, D, Frequencies of the different edited isoforms detected (wildtypes, N = 94; nulls, N = 93). Fifteen isoforms were detected, and 14 of them were not significantly altered in the absence of PSD-95. There is a significant increase in the proportion of the VSI isoform in PSD-95null mouse hippocampus. All mRNA editing data are plotted as the frequency expressed as a fraction of the total, ± the SEM. Normalized mRNA measurements are presented as means ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; one-tailed unpaired t test for the comparison of mRNA levels and one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls post hoc tests for comparison of the mRNA editing measurements.