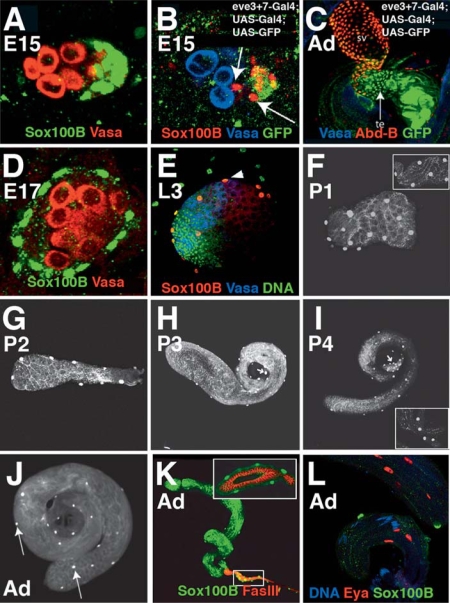
Fig. 1.
Expression of Sox100B in the testis. In this and subsequent figures, the colors for each antibody staining are indicated by the colored text in each panel. A Wild type stage 15 embryonic testis stained with anti-Vasa to mark the germline and anti-Sox100B revealing the male-specific somatic gonadal precursors (msSGPs). B In eve3 + 7-Gal4;UAS-Gal4;UAS-GFP stage 15 gonads from male embryos, GFP and Sox100B mostly co-localize although some Sox100B expressing cells are negative for GFP (arrows) indicating they originate outside parasegment 13. C In the adult testis the GFP from the eve3 + 7-Gal4;UAS-Gal4;UAS-GFP reporter labels terminal epithelium (te) in addition to seminal vesicle (sv), which is also labeled with Abd-B, and other genital disc-derived structures. D Wild type embryonic testis at stage 17 revealing the germ line and the Sox100B positive superficial cells coating the gonad, the pigment cell precursors. E Third larval instar testis stained to reveal the germ line, DNA and Sox100B. Note the staining in the superficial pigment cells with their characteristic large nuclei (arrowhead). F–J Anti-Sox100B staining during testis morphogenesis: day 1 pupal testis (F), day 2 pupal testis (G), day 3 pupal testis (H), day 4 pupal testis (I), adult testis (J) showing the continued expression of Sox100B in pigment cells (inserts in F and I, and arrows in J focus on pigment cell nuclei). K The accumulation of Sox100B expressing cells at the basal end of the testis marks the terminal filament as revealed by staining with anti-FasIII, the insert shows an optical section demonstrating that the pigment cells lie over the terminal epithelium. L Sox100B does not co-localize with the somatic cyst cell marker Eya. Developmental stages of selected testes are indicated. E15, E17 = stage 15 or 17 embryos; L3 = late third instar larva; P1–4 = days of pupal development; Ad = adult.