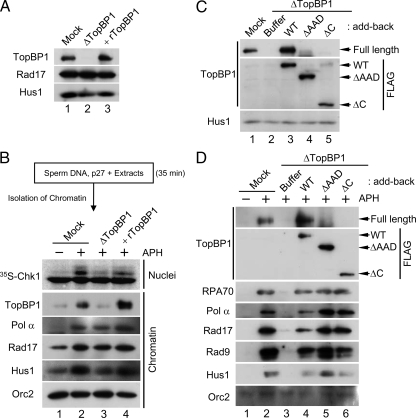
Figure 5.
Initial binding of the N-terminal half of TopBP1 to chromatin is sufficient for the formation of replication forks. (A) Mock-depleted extracts (lane 1) and TopBP1-depleted extracts supplemented with buffer alone (lane 2) or rTopBP1 (lane 3) were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. (B) Sperm chromatin was isolated after a 35-min incubation in egg extracts in the presence of 2 μM p27. Next, the p27-treated chromatin was transferred to mock-depleted extracts (lanes 1 and 2) or TopBP1-depleted extracts supplemented with buffer (lane 3) or rTopBP1 (lane 4). Extracts were incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence of aphidicolin (lanes 2–4). Aliquots of the extracts were incubated with 35S-Chk1. Nuclear fractions from these incubations were processed for phosphorimaging (top panel). Other aliquots were processed for isolation of chromatin fractions and immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (bottom panels). (C) Mock-depleted extracts (lane 1) and TopBP1-depleted extracts supplemented with buffer (lanes 2) or the indicated versions of recombinant TopBP1 (lanes 3–5) were immunoblotted with anti-TopBP1 (top), anti-FLAG (middle), and anti-Hus1 antibodies (bottom). (D) Chromatin fractions from the extracts in C were immunoblotted with anti-TopBP1 antibodies (top panel), anti-FLAG antibodies (second panel from top), and the additional indicated antibodies (bottom panels).