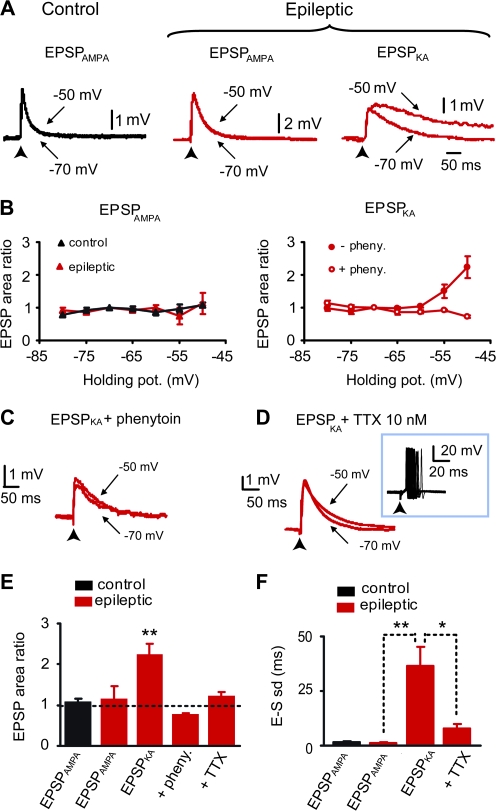
Figure 3.
Voltage-dependent amplification of EPSPKA but not EPSPAMPA via the activation of persistent sodium current. (A) Superimposed average evoked subthreshold EPSPAMPA recorded at threshold holding potential (−50 mV) and at Vrest (−70 mV) in granule cells from control (left, black traces) and epileptic rats (middle, red traces, in the presence of 10 μM SYM 2081); superimposed average evoked subthreshold EPSPKA recorded in a granule cell from an epileptic rat (right, red traces, in the presence of 100 μM GYKI 52466). (B) Scatter plot of mean amplification (ratio of EPSP area at −50 vs. −70 mV) versus membrane potential. Note that EPSPAMPA are not amplified with depolarization (left graph), both in control (black triangles, n = 5 cells) and in epileptic rats (red triangles, n = 5 cells); on the contrary, EPSPKA in epileptic rat (right graph) are significantly amplified with depolarization (filled circles, n = 8 cells). This amplification is completely prevented by phenytoin (100–200 μM, open circles, n = 5 cells). (C) Superimposed evoked EPSPKA recorded in the presence of phenytoin (200 μM) in epileptic rat at −50 and −70 mV. Note that the voltage-dependent amplification is completely abolished when persistent sodium current is blocked by phenytoin. (D) Superimposed evoked EPSPKA recorded in the presence of low concentration of TTX (10 nM) in epileptic rat at −50 and −70 mV. Note that the voltage-dependent amplification is completely abolished when persistent sodium current is blocked by TTX. Trace inset shows that 10 nM TTX does not prevent neuronal firing and increases spike timing reliability. (E) Bar graph of the mean amplification (ratio of EPSP area at −50 vs. −70 mV) for EPSPAMPA in control (n = 11 cells), EPSPAMPA in SYM 2081 in epileptic rats (n = 5 cells), EPSPKA in GYKI 52466 in epileptic rats (n = 13 cells, **P < 0.01), EPSPKA in the presence of phenytoin in epileptic rats (n = 5 cells), and EPSPKA in the presence of 10 nM TTX in epileptic rats (n = 6 cells). (F) Bar graph of EPSP-spike latency SD for EPSPAMPA in control (n = 20 cells), EPSPAMPA in SYM 2081 in epileptic rats (n = 5 cells), EPSPKA in GYKI 52466 in epileptic rats (n = 17 cells, **P < 0.01), and EPSPKA in the presence of 10 nM TTX in epileptic rats (n = 7 cells, *P < 0.05).