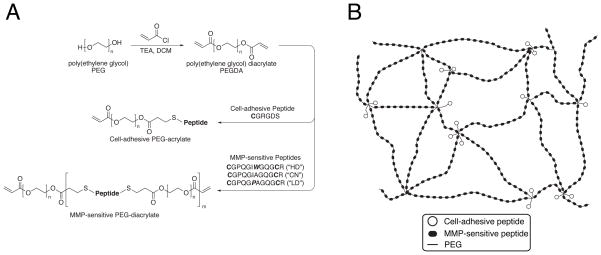
Figure 1.
(a) Synthetic scheme. PEG 3400 is reacted with acryloyl chloride to form PEGDA, which is then reacted with cysteine-bearing peptides via Michael-type addition to form cell-adhesive or, in a separate reaction, MMP-sensitive PEG-acrylate macromers. Reaction stoichiometry controls the molecular weight and polydispersity of the resultant species during step-growth polymerization. (b) Schematic illustration of hydrogel structure. Photopolymerization of the photoactive precursors from (a) yields bioactive hydrogels with multiple MMP-sensitive peptides per backbone chain, with pendant cell-adhesive ligands tethered from sites of acrylate crosslinking.