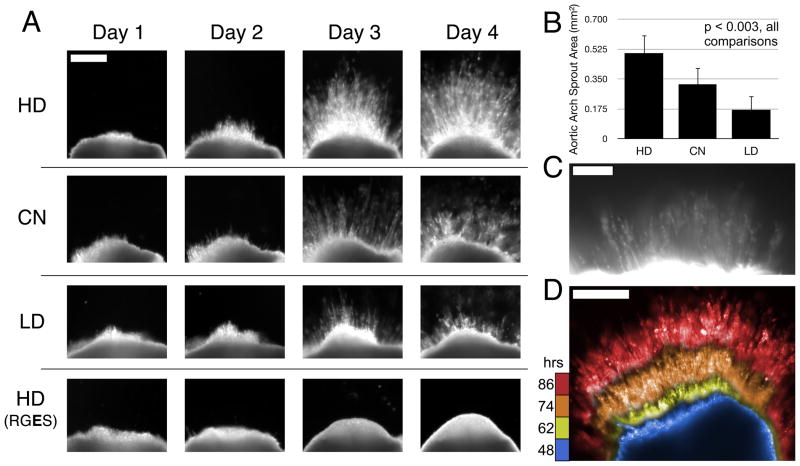
Figure 5.
(a) Representative images of chick aortic arch ring explants sprouting into hydrogels over time. In 8-wt% gels with 1.0 μmol/mL CGRGDS density, angiogenic sprouting varies with the MMP-susceptibility of the hydrogel backbone. No detectable sprouting occurred in negative control hydrogels containing RGES instead of RGDS peptide. Scale bar for all images = 250 μm. (b) Quantification of sprout area at Day 4, n=6 per condition. Mean with standard deviation, all comparisons are significant, p < 0.003 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD post-hoc testing. (c) Fluorescent staining with lectin-rhodamine implicates endothelial cells as a principal component of the angiogenic sprouts in these hydrogels. Scale Bar = 100 μm. (d) Composite image of selected frames during sprouting time-course by dark field imaging (see supplemental Movie 1), false colored then overlaid here to aid in time visualization. Blue, yellow, orange, red = 48, 62, 74, 86 hours respectively. Scale Bar = 250 μm.