Fig. 4. Pharmacological inhibition or shRNA-mediated suppression of Chk1 abrogates G2/M arrest following exposure to curcumin.
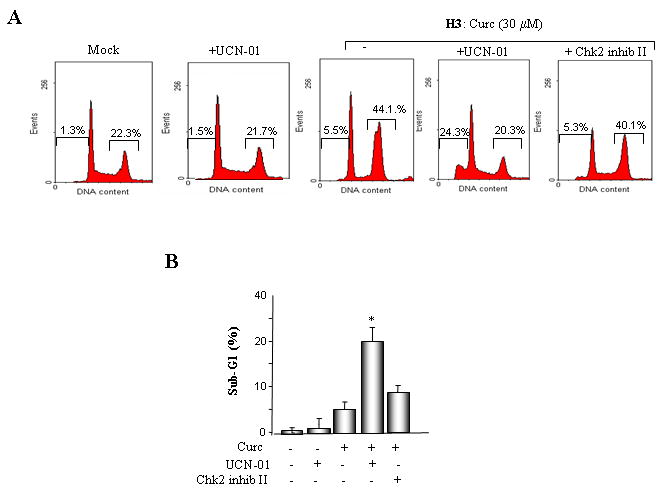
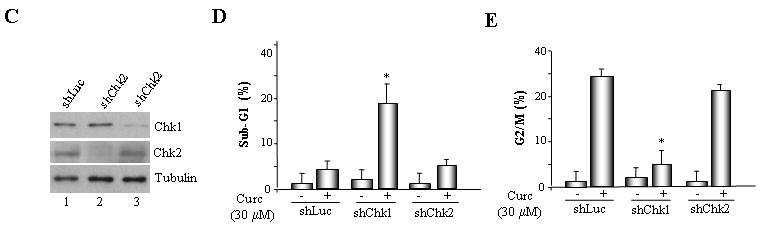
A. MLH1-proficient (HCT116+ch3; H3) cells were pre-incubated with UCN-01 or Chk2 inhibitor II and subsequently mock treated or exposed to curcumin (30 μM). Additionally, HCT116+ch3 cells were either untreated or treated with UCN-01 only. DNA content was measured 36 h post-treatment by PI staining/flow cytometry. Percentage of cells with 4N (G2/M) and sub-G1 DNA content is indicated. B. Graphed is the percentage of cells displaying sub-G1 DNA content in curcumin-treated H3 cells in the presence and absence of UCN-01 or Chk2 inhibitor II. The mean of three independent experiments is indicated, error bars= +1 SD. *denotes P<0.01. C. ShLuc, shChk1 or shChk2 cell lysates were immunoblotted with Chk1 (top), Chk2 (middle) or tubulin (bottom) antibodies. D. ShLuc, shChk1 and shChk2 cells were either mock (DMSO) treated or exposed to curcumin (30 μM) and 36 h later DNA content in the cell population was quantified by PI staining/flow cytometry. Graphed is the mean percentage of sub-G1 cell population from three independent experiments, error bar = +1 SD. *denotes P<0.01. E. ShLuc, shChk1 and shChk2 cells were either mock (DMSO) treated or exposed to curcumin (30 μM) and 36 h later DNA content in the cell population was quantified by PI staining/flow cytometry. Graphed is the mean percentage of G2/M cell population from three independent experiments, error bar = +1 SD. *denotes P<0.01.
