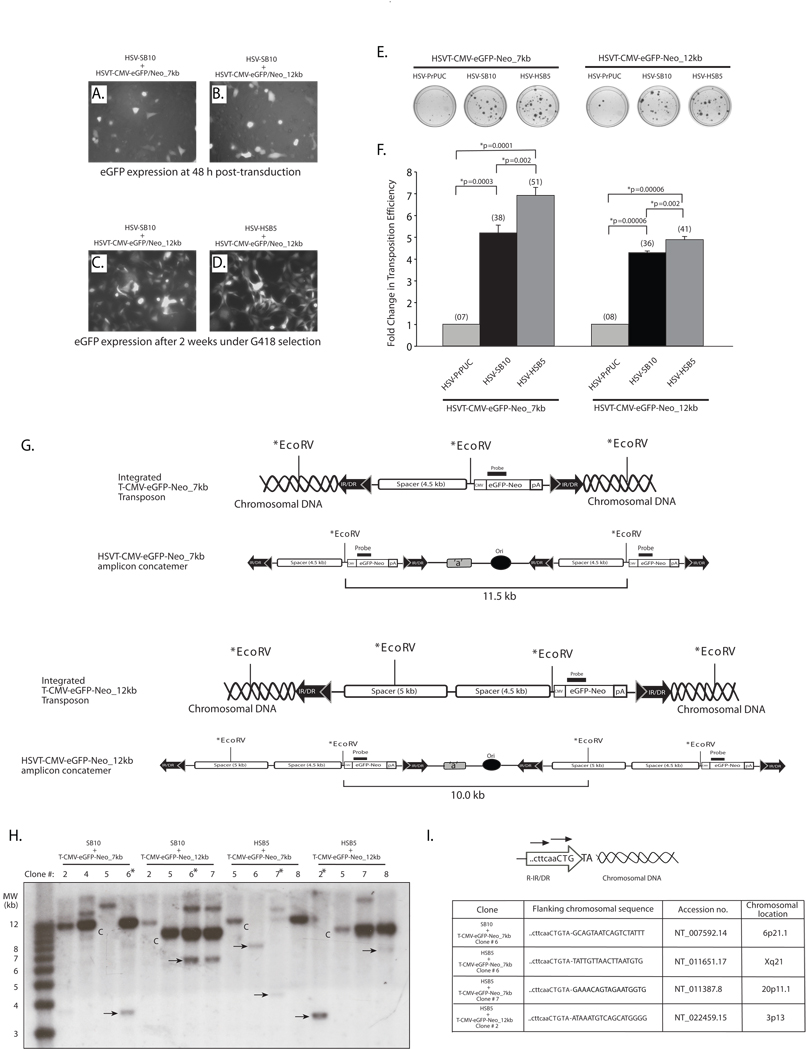
Figure 3. The SB transposase is competent in efficiently mobilizing a 12-kb transposable unit from the context of an HSV amplicon vector.
HeLa cells (1×105 cells/well) were co-transduced with HSV amplicon vectors expressing either the “wild-type” SB transposase (HSV-SB10) or the hyperactive HSB5 transposase (HSV-HSB5), together with either the HSVT-CMV-eGFP/Neo_7kb amplicon or the HSVT-CMV-eGFP/Neo_12kb amplicon at an MOI of 1.0. Upon incubation for 1 h at 37°C, the virus-containing medium was removed and cells were washed once and replenished with fresh media. (A–B) Enhance GFP expression was assessed 48 h post-transduction via fluorescence microscopy to determine the transduction efficiency of the HSVT-CMV-eGFP/Neo_7kb and HSVT-CMV-eGFP/Neo_12kb amplicons in the presence of the co-delivered SB-expressing amplicon vector. Subsequently, the cells were trypsinized and seeded at a 1:3 dilution on 100-mm dishes and placed under 600 µg/ml G418 selection for a period of 2 weeks. (C–D) After 2 weeks, G418-resistant colonies were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and analyzed via fluorescence microscopy for eGFP expression. Representative images of G418-resistant colonies 2 weeks post-transduction of HSVT-CMV-eGFP/Neo_12kb either with HSV-SB10 or HSV-SB12 are shown. (E) Upon confirmation of eGFP expression, the G418-resistant colonies were stained with 2% methylene blue, washed extensively with dH2O, and blue colonies were enumerated. (F) The transposition efficiency of SB10 and HSB5 in the presence of either the 7- or 12-kb transposon-harboring HSVT amplicons is represented as a fold-change in the number of G418-resistant colonies compared to when SB transposase was absent (HSVPrPUC control amplicon). The average number of G418-resistant colonies (n=3) corresponding to each group is indicated in parentheses above each bar in the histogram. Error bars represent standard error. Statistical analysis was conducted using the student t-test and p values are indicated. (G) Schematic representations of integrated configurations of the T-CMV-eGFP-Neo_7kb and T-CMV-eGFP-Neo_12kb transgenons and their concatemeric amplicon genome counterparts. The relative locations of signature EcoRV restriction enzyme recognition sites and the location of a DNA probe used in subsequent Southern blot analyses are depicted. (H) Similarly, G418-resistant colonies that were co-transduced with either HSV-SB10 or HSV-HSB5 and HSVT-CMV-eGFP/Neo_7kb or HSVT-CMV-eGFP/Neo_12kb were trypsinized and expanded in 60-mm dishes for the purpose of isolating genomic DNA for Southern blot analysis to determine chromosomal integration of the 7- and 12-kb transposons. Once confluent, these transduced HeLa cell monolayers were lysed using lysis buffer (10 mM Tris.Cl, 100 mM NaCl, 25 mM EDTA and 0.5% SDS) and genomic DNA was isolated using phenol:chloroform extraction followed by ethanol precipitation. Ten micrograms of genomic DNA was digested with EcoRV, which cuts once within the 7-kb transposable unit 5’ of the CMV-eGFP-Neo transcription unit and twice within the 12-kb transposable unit. The digested genomic DNA was electrophoresed on a 0.8% TAE agarose gel and transferred onto a nylon membrane, UV cross-linked and probed with a α-32P-dCTP-radiolabeled eGFP/Neo probe (917-bp), which was obtained by excising the eGFP-Neo fragment from the pBSFBR-CMV-eGFP-Neo vector using Pst1 and BamHI. The 1-kb plus DNA ladder (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was radiolabeled according to manufacturer recommendations (Lane 1). “C” indicates HSV amplicon units generated by EcoRV digestion of the episomal HSV amplicon concatemer or integrated concatemeric transgenon units, while the ‘arrows’ indicate predicted SB-mediated integration events within the HeLa cell genome and “*” demarcates clones later analyzed by integration site mapping. (I) To determine the integration sites of the 7-kb and 12-kb transposable units within the HeLa cell genome, linker-mediated PCR (LM-PCR) analysis was conducted using the GenomeWalker™ Universal Kit (Clontech, Mountain view, CA) according to manufacturer recommendations. Chromosomal sequences flanking the right IR/DR junction of the 7- and 12-kb transposable units were PCR amplified from genomic DNA samples that were analyzed by Southern blotting using a nested primer set described in Largaespada et al.,25 and cloned into the TOPO-TA vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) for subsequent sequence analysis.