Figure 4.
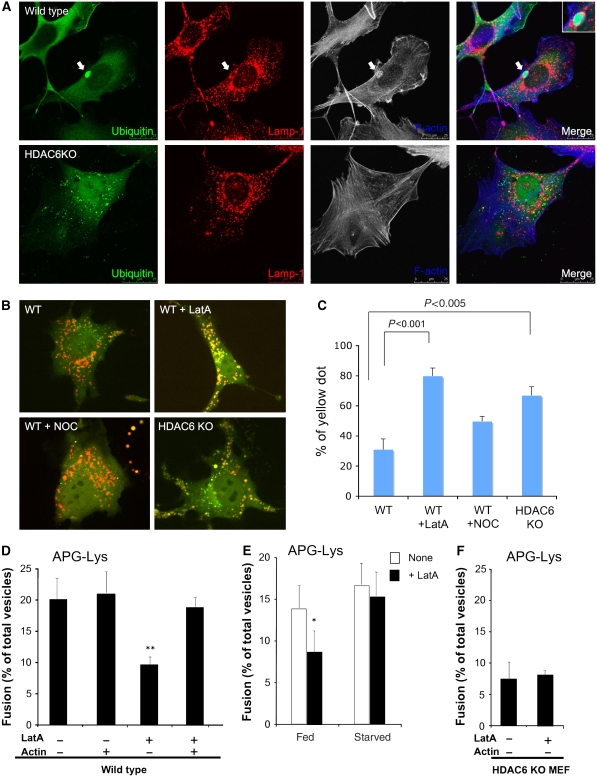
Actin remodelling is required for autophagosome–lysosome fusion under basal conditions. (A) Wild-type and HDAC6 KO MEFs were treated with MG132 and immunostained with antibodies to Lamp-1 (a lysosome marker, red) and ubiquitin (green) as indicated. F-actin was detected by phalloidin (blue). The arrows indicate ubiquitin-positive aggregates that are surrounded by F-actin and Lamp-1. (B, C) Wild-type and HDAC6 KO MEFs were transfected with mCherry-GFP-LC3, followed by treatment with LatA (100 nM) or nocodazole (250 nM) for 6 h and analysed as described in Figure 3A. (D) Autophagosomes (APGs) and lysosomes (Lys) isolated from fed mouse hepatocytes were treated or not with latrunculin (LatA) as indicated, extensively washed to remove traces of the inhibitor, and then labelled with the antibody and subjected to in vitro fusion assay in the presence or absence of purified actin. The number of total fusion events/total number of vesicles for each condition was as follows: 176/880; 233/1110; 84/930; and 180/950. The differences with untreated samples were significant at **P<0.01. (E) Autophagosomes (APGs) and lysosomes (Lys) isolated from fed or starved mouse hepatocytes were treated or not with latrunculin (LatA) as labelled and subjected to in vitro fusion assay. The differences with untreated samples were significant at *P<0.05. The number of total fusion events/total number of vesicles for each condition was as follows: 169/1250; 87/972; 190/1120; and 175/1165. (F) Autophagosomes (APGs) and lysosomes (Lys) isolated from HDAC6 KO MEFs were treated or not with latrunculin (LatA) as indicated and subjected to in vitro fusion assay.