Figure 1.
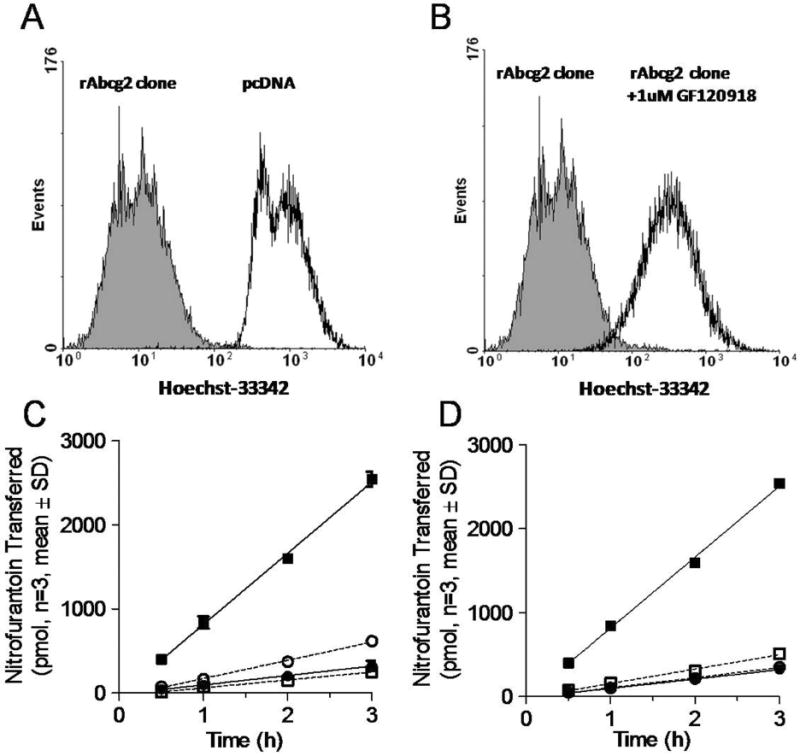
Functional characterization of MDCKII-rat Abcg2 expressed cells. The Hoechst 33342 accumulation of MDCKII cells with either empty vector (black unfilled) or rAcbg2 clone cells (shaded) (Panel A). Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry following incubation of the ABCG2 substrate Hoescht 33342 in presence (black unfilled) and absence (shaded) of 1 μM of the ABCG2 inhibitor, GF120918 (Panel B). The amount of nitrofurantoin appearing in the receiver compartment across MDCKII-empty vector and MDCKII-rAbcg2 monolayers grown on Transwells (Panels C and D). Panel C depicts the flux of nitrofurantoin from the basolateral to apical (●■); apical to basolateral (○□) in MDCKII-empty (●○) and MDCKII –Abcg2 (□■); Panel D depicts the transport of nitrofurantoin from the basolateral to apical in MDCKII-empty (●○) and MDCKII –Abcg2 (□■) in MDCKII-rAbcg2 absence (●■) or presence (○□) of 1 μM GF120918.
