Abstract
The autosomal-dominant precancerous condition familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is caused by germline mutations in the tumour suppressor gene APC. Consistent correlations between the site of mutations in the gene and clinical phenotype have been published for different patient groups. We report our experiences of APC mutation analysis and genotype-phenotype correlations in 1166 unrelated polyposis families and discuss our results in the light of literature data. We show that the mutation detection rates largely depend on the family history and clinical course of the disease. We present a list of 315 different point mutations and 37 large deletions detected in 634 of the 1166 index patients. Our results confirm previously published genotype-phenotype correlations with respect to the colorectal phenotype and extracolonic manifestations. However, 'exceptions to the rule' are also observed, and possible explanations for this are discussed. The discovery of autosomal-recessive MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP) as a differential diagnosis to FAP implies that some results have to be reinterpreted and surveillance guidelines in the families have to be reevaluated.
Keywords: familial adenomatous polyposis, APC gene, APC mutations, genotype-phenotype correlations
Introduction
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP, OMIM +175100) is a clinical diagnosis that is typically based on the presence of more than 100 colorectal adenomas. If untreated patients develop colorectal cancer at a mean age of 40 years [1]. Other gastrointestinal features (duodenal adenomas, fundic gland cysts) and extragastrointestinal manifestations, including congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), desmoids and osteomas are frequently described.
FAP is an autosomal-dominant disorder caused by germline mutations in the tumour suppressor gene APC on chromosomal region 5q22 [2,3]. The APC gene encodes a multifunctional protein of 2843 amino acids that plays a major role in controlling cell cycle progression, migration, differentiation and apoptosis (review in [4,5]). Germline mutations in the APC gene were also detected in some families with an attenuated polyposis phenotype (AAPC, AFAP) who present with less than 100 adenomas and a later age at onset compared to patients with typical FAP [6].
During the last few years correlations between site of mutation in the APC gene and clinical phenotype have been reported on patient groups of different sizes [7-12]. Most of the published correlations proved to be statistically consistent, but there were also 'deviations from the rule' when individual cases were considered.
Recently a polyposis syndrome characterised by multiple adenomatous polyps and an autosomal-recessive mode of inheritance has been identified that is caused by germline mutations in the base excision repair gene MUTYH (MYH) [13]. Biallelic MUTYH mutations have been identified in up to 40% of patients in whom no mutation in the APC gene was identified [14-16]. This new adenomatous polyposis condition is designated as MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP; OMIM #608456) and has to be considered as a differential diagnosis of the autosomal-dominant FAP.
In this review we report on our experience of mutation analysis in the APC gene and genotype-phenotype correlations in 1166 unrelated patients with a clinical diagnosis of FAP or multiple adenomatous polyposis consistent with AAPC and discuss our results in the light of literature data.
Phenotype classification
Since 1991, blood samples from 1166 unrelated patients with a clinical diagnosis of typical or attenuated FAP (AAPC) have been referred to the Institute of Human Genetics, University of Bonn for mutation analysis in the APC gene. Clinical information on 2066 patients from the 1166 families was obtained during genetic counselling sessions, from a questionnaire, or through telephone interviews and/or medical records. The study was approved by the Ethics Commission of University Hospital, Bonn.
Colorectal phenotype
The classification of different FAP phenotypes was based on the number of colorectal adenomas, age at diagnosis of FAP and occurrence of CRC (Table 1). The FAP phenotype was classified as typical when the patient presented with more than 100 colorectal adenomas before the age of 35; in cases of unavailable or unclear colonoscopic data, the classification was based on the occurrence of clinical bowel symptoms before the age of 35, or a diagnosis of CRC before the age of 45. The diagnostic criterion for the attenuated phenotype (AAPC) was the occurrence of a smaller number of adenomas (10-100) after the age of 25 or more than 100 adenomas diagnosed for the first time after the age of 45. When the polyp number was unknown, AAPC was assigned if the first symptoms or diagnosis of CRC occurred after the age of 45. The phenotype was considered severe in patients who developed more than a thousand adenomas or polyposis-related bowel symptoms before the age of 15, or when diagnosed with polyps before the age of 10. The phenotype was classified as atypical in patients who did not meet the criteria for either typical or attenuated FAP, when an unambiguous attribution was impossible. Patients with an atypical course usually presented with more than 100 polyps, diagnosed between 35 and 45 years of age; in addition, cases with an obvious discrepancy between the age at diagnosis (symptoms) and the number of colorectal adenomas were also considered atypical. If clinical information on the colorectal disease was not available or not sufficient to determine the extent of colorectal polyposis, the phenotype was considered 'unknown'.
Table 1.
APC mutation detection rate according to colorectal phenotype and family history
| Colorectal phenotype | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| all | severe | typical | atypical | attenuated | unknown | |
| Patients | 1166 | 33 | 504 | 85 | 407 | 137 |
| point mutation | 597 | 25 | 384 | 38 | 93 | 57 |
| large deletion | 37 | 30 | 2 | 4 | 1 | |
| all mutations | 634 | 25 | 414 | 40 | 97 | 58 |
| Mutation detection rate | 54% | 76% | 82% | 47% | 24% | 42% |
| Familial cases (dominant) | 558 | 13 | 326 | 38 | 131 | 50 |
| Mutation detection rate | 73% | 85% | 85% | 71% | 49% | 56% |
| Familial cases (recessive) | 27 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 17 | 1 |
| Mutation detection rate | 0% | |||||
| De novo mutations | 63 | 10 | 46 | - | 6 | 1* |
| Mutation detection rate | 100% | |||||
| Single cases | 255 | 7 | 65 | 26 | 127 | 30 |
| Mutation detection rate | 30% | 43% | 60% | 27% | 14% | 30% |
| Unknown | 263 | 2 | 66 | 15 | 125 | 55 |
| Mutation detection rate | 34% | 50% | 80% | 40% | 7% | 36% |
* The diagnosis of FAP was suspected because of osteomas in a child with normal colonic phenotype at the age of 11. In this patient a de novo frameshift mutation in codon 1551 was proven.
Family history
Due to the existence of the recently discovered MUTYH-associated polyposis [13] we considered it important to allow for the mode of inheritance in the families: index patients were classified as familial cases with autosomal-dominant inheritance when at least two patients (one of them a parent of the index patient) were affected in the family. An autosomal-recessive mode of inheritance was considered when the index patient had at least one affected sibling, but no affected parents or children. Cases where the index patient was the only affected person known in the family, or no information on other family members (parents, siblings, children) was available, were classified as 'single cases'. Index patients were classified as de novo mutations only if an APC mutation was identified and both parents were either healthy until an advanced age, or when the mutation was excluded in both parents, irrespective of whether or not the index patient had affected children [17].
Mutation analysis in the APC gene
Point mutations
Genomic DNA extracted from peripheral blood samples was used for mutation analysis. We started the search for germline mutations in the APC gene in 1991 by SSCP and heteroduplex analysis. To date, we apply the protein truncation test (PTT) for detection of mutations in exon 15 in four overlapping fragments, essentially as described [18], using an in vitro transcription translation kit (Promega, Mannheim, Germany) in the presence of 35S-Methionine (Amersham). Denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) is used for screening of exons 1-14 and the first 400 bp of exon 15 (WAVE, Transgenomics). PCR fragments showing variant bands by either method were sequenced on an ABI prism 377 or ABI 3100 automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Darmstadt, Germany) using the cycle sequencing procedure and the BigDye terminator kit version 2.0 or 1.1, respectively. Some of the APC mutation negative patients from the first series were reexamined using the more up-to-date procedures described.
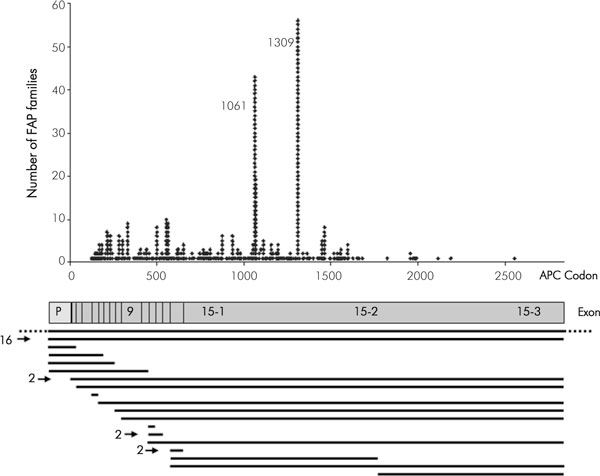
We identified a germline point mutation in the APC gene in 597/1166 patients (51.2%) (Table 1). Overall, we found 315 different point mutations (Supplementary table 1). Most of the mutations are spread over the first half of the gene. Of note, no mutation was detected in exons 1 and 2 (Fig. 1). Two hot spot mutations at codons 1309 and 1061 are evident.
Figure 1.
Distribution of 597 germline point mutations and 37 large deletions in the APC gene detected in 634 out of 1166 unrelated FAP patients. A schematic diagram presents the promotor region (P) and the 15 exons of the APC gene. The black horizontal bars represent the extent of deletions as determined by MLPA, and the numbers on the left side of the bars indicate the deletions that have been identified more than once (details in [20]). The bar with dotted lines indicates a cytogenetically detectable deletion.
Most mutations were truncating, including 364 frameshift mutations, 182 nonsense mutations and 38 mutations in the highly conserved splice site sequences. In addition, in 13 patients we identified 8 different missense mutations and three different silent substitutions; seven of these single base substitutions were localised at exonic boundaries. For four substitutions localised in exon 4 and exon 14 we could demonstrate by RNA analysis that they actually affect splicing and thus cannot be considered missense mutations or silent variants [19].
Large genomic deletions
DNA samples from patients negative for point mutations in the APC gene were examined for the presence of large genomic deletions or duplications using MLPA (multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification) (SALSA P043 APC exon deletion test kit; MRC Holland, Amsterdam) according to the manufacturer's recommendations, as described [20].
Five large genomic deletions encompassing the APC gene had been detected earlier by haplotype analysis; one of them was cytogenetically visible [21,22]. By use of MLPA we have examined so far 401 out of the 569 patients negative for point mutations in the APC gene for the presence of large genomic deletions or duplications [20]. Altogether we have detected a total of 37 large deletions. The deletions extend over single exons up to the entire APC gene including the promotor region (see Supplementary table 2 and Fig. 1).
Mutational hot spots
The 5 bp deletion c. 3927_3931delAAAGA (at codon 1309) was detected in 56 of the 1166 index patients (4.8%). All except two patients with this mutation showed typical or severe early onset polyposis; in this combined patient group the frequency of the 1309 mutation increases to 10% (54/537). The mutation occurs at high frequency de novo: in 22 of the 56 index patients (39%) the 5 bp deletion at codon 1309 was excluded in both parents [17]. In the two patients diagnosed at ages of 43 and 53, the mutation had occurred de novo as well. This mutation was also reported at high frequencies in patients from Japan, Singapore and South Africa [23-25] and at moderate proportions in most European populations [26-29], but - interestingly - it has not been found in patient groups from Australia or Spain [30,31].
The hot spot mutation c. 3183_3187delACAAA (at codon 1061) was detected in 43 index patients: 3.7% of all patients and 7.1% (36/504) in the group of patients with typical FAP. This mutation occurred de novo in 7 of the 43 index patients (16.3%).
Mutation detection rate according to phenotype and family history
APC mutation detection rates in FAP patients varying between 30-85% have been published [26-29,32]. For evaluation of the APC mutation detection rate and prevalence of mutations it is worthwhile to consider the colorectal phenotype and the family history of index patients examined for mutations. Overall, point mutations and large deletions in the APC gene were detected in 634 of the 1166 index patients (54%) (Table 1). The mutation detection rate was 82% in patients with typical FAP, but only 24% in patients with AAPC. Remarkably, 30 of the large genomic deletions (81%) occurred in patients with typical FAP.
The distribution of patients according to family history and the corresponding mutation detection rates are presented in Table 1. As expected, the mutation detection rate increases in all patient groups when only familial cases with an autosomal-dominant mode of inheritance are considered (Table 1). The mutation detection rate in cases with de novo mutations is - by our definition - 100%. Most of the patients with a de novo mutation had developed typical FAP.
Genotype-phenotype correlations
For evaluation of the correlation between the site of mutation in the APC gene and different colonic and extracolonic manifestations we included clinical information obtained from 2066 patients from the 1166 families.]
CHRPE
Presence of CHRPE has been reported in patients with mutations 3' to exon 9 [9,10] but not beyond codon 1444 [8,33]. However, isolated cases constituting exceptions to this 'rule' have also been published [34].
Information on the results of retinal examination was available for 413 patients from 285 families with known germline mutations (Table 2). Since patients with mutations in exon 9 were published both with and without CHRPE, we defined the limit of the region characteristic for CHRPE in codon 410, the first codon outside the alternatively spliced sequence of exon 9.
Table 2.
Relationship between the site of mutation in the APC gene and CHRPE status in 413 FAP patients from 285 families. The patients whose CHRPE status conforms to the published correlation are printed in bold.
| Site of APC mutation (Codon) | Predicted CHRPE status | Number of patients examined for CHRPE | Number of patients with CHRPE | Number of patients without CHRPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 122-414 | CHRPE-negative | 52 (39) ** | 6 (6) | 46 (34) |
| 423-1367 | CHRPE-positive | 307 (205) | 244 (156) | 63 (58) |
| 1451-2557 | CHRPE-negative | 34 (29) | 3 (3) | 31 (28) |
| large deletions* | ? | 20 (12) | 15 (9) | 5 (5) |
| all patients | 413 (285) | 268 (174) | 145 (118) | |
*Patients with large deletions encompassing the whole gene were in both CHRPE-positive and CHRPE-negative groups.
**The numbers of families are shown in parentheses. In some families a discrepant CHRPE status was observed.
Overall, CHRPE was detected in 268 of the 413 patients (65%), including 15 patients from 9 families with large deletions. 244 of the 253 CHRPE-positive patients with point mutations in the APC gene (96%) had mutations between codons 423-1367. However, 63 of the 307 patients with mutations in this part of the gene (21%) did not present CHRPE, and thus do not conform to the previously published correlation. On the other hand, 76 out of the 85 patients (89%) with mutations between codons 122-414 or 1451-2557 did not have CHRPE; thus, only nine patients did not conform to the published rule. CHRPE was detected in 15 out of 20 patients with large deletions. Of note, deletions of the entire APC gene were detected in both CHRPE-positive and CHRPE-negative groups.
Taken together, the previously published correlation between site of mutation and expression of CHRPE was confirmed in our large group of patients, but overall 18% of patients with point mutations (63+9/393) do not conform to the rule. Part of this deviation might be explained by the fact that some patients were seen by ophthalmologists who are not aware of the different types of CHRPE, including even small retinal lesions [35]. However, intrafamilial discrepant observations were also found in some patients who were examined by an ophthalmologist experienced in diagnosis of CHRPE over several years. Of note, 12 out of the 63 CHRPE-negative patients (19%) with mutations within codons 423-1367, but only 21 of the 244 CHRPE-positive patients (9%) had a de novo mutation (p = 0.023; Fisher's exact test, two sided), suggesting that CHRPE may not be expressed in some patients with de novo mutations because of somatic mosaicism.
Colorectal phenotype
According to data from the literature, a severe clinical phenotype is associated with mutations at codon 1309 [7,12], and an attenuated FAP is observed in patients with mutations 5' to codon 168 [6], in the alternatively spliced sequence of exon 9 [11,36-39] or 3' to codon 1580 [40-42] while typical FAP is observed in patients with mutations at the remaining sites.
Progression of colorectal disease in FAP patients is a continuous process. Therefore, evaluation of the severity of the disease is largely dependent on time of diagnosis. The most accurate parameters for evaluation of the natural course of the disease would be the age at occurrence of the first colonic adenomas and the age-related number of polyps. However, these data are available only for a small number of mutation carriers who started with regular colonoscopies at an early age.
Age at diagnosis of adenomas in asymptomatic mutation carriers who underwent endoscopic screening is not a suitable parameter as it depends on the time of the first endoscopy and whether surveillance is regularly performed. Therefore, we used the age at diagnosis of FAP in patients who developed gastrointestinal symptoms (rectal bleeding, diarrhoea, etc.) prior to the first endoscopies as a parameter for the severity of the colorectal phenotype [28]. Age at diagnosis of FAP was known in 760 patients who were diagnosed after the onset of bowel symptoms (Fig. 2). The mean age at diagnosis in these patients was 35 years (range 3-78 years). Germline mutations in the APC gene were identified in 485 of the 760 patients diagnosed because of bowel symptoms. We confirmed in these patients the correlation between APC mutation site and mean age at diagnosis of FAP (Fig. 2). Patients with a mutation at codon 1309 developed bowel symptoms more than 10 years earlier (20 years of age) compared with patients with other mutations: 50 years of age in patients with mutations at sites characteristic of AAPC, 32 years of age in patients with mutations at other sites and 41 years of age in patients with no identified APC mutation (p < 0.001 for all comparisons; two-sided Student's t-test). The 32 patients with large genomic deletions had a mean age at diagnosis of 33 years, comparable to that of patients with mutations characteristic of typical FAP (p = 0.38). Despite this significant correlation a considerable variation of age at diagnosis in patients with the same mutation or even within the same family was observed, as we had illustrated for part of this patient group in a previous report [28].
Figure 2.
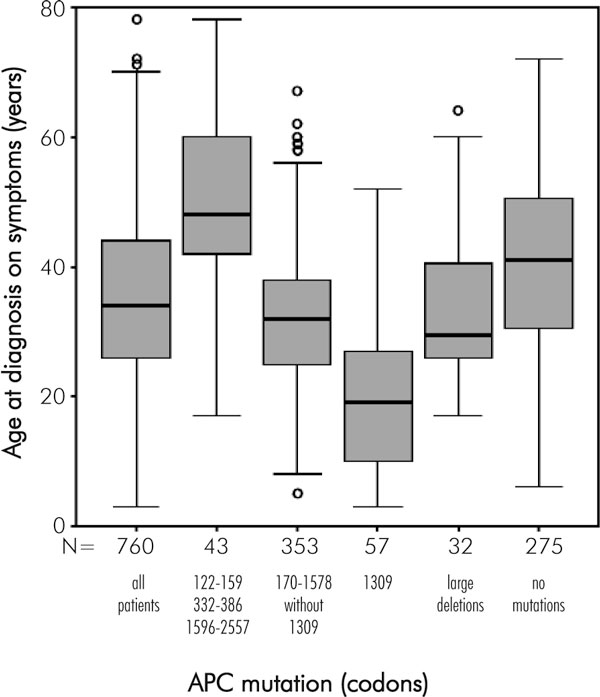
Box plot showing the relationship between the mutation site in the APC gene and age at diagnosis (achieved after bowel symptoms had developed) in 485 patients with known mutations and 275 patients with unknown mutations. The black horizontal bars represent the median age at diagnosis.
As another parameter for severity of the disease we used the clinical phenotype classification that takes into account the age-related polyp number in addition to the age at diagnosis (see phenotype classification).
When grouping the 2066 patients according to the clinical phenotype and the mutation intervals outlined above, most patients conformed to the published genotype-phenotype correlation (Table 3): 84 of the 101 patients with mutations at sites characteristic of AAPC (83%) were classified as having an attenuated phenotype, and another 8 patients had an atypical phenotype. Accordingly, 80% of patients with mutations at sites characteristic of typical FAP (587/735) were classified as having a typical FAP phenotype. Only 34% (28/83) of patients with mutations at codon 1309 were classified as having a severe phenotype, whereas 63% (52/83) had typical FAP.
Table 3.
Grouping of patients classified according to the site of APC mutation and colorectal phenotype. The numbers of patients with the expected phenotype at the respective germline mutation region are printed in bold
| Colorectal phenotype | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site of APC mutation (Codon) | Predicted phenotype | All patients | known | severe | typical | atypical | attenuated | unknown |
| 122-161 314-405 1581-2557 |
Attenuated FAP | 146 | 101 | 9 | 8 | 84 | 45 | |
| 170-1578 without 1309 |
Typical FAP | 1059 | 735 | 34 | 587 | 46 | 68 | 324 |
| 1309 | Severe FAP | 96 | 83 | 28 | 52 | 1 | 2 | 13 |
| Large deletions | ? | 78 | 67 | 57 | 4 | 6 | 11 | |
| No mutation | ? | 687 | 540 | 12 | 123 | 52 | 353 | 147 |
| All | 2066 | 1526 | 74 | 828 | 111 | 513 | 540 | |
Influence of mutation type on clinical phenotype
The genotype-phenotype correlations presented here and in reports on other patient groups roughly consider only the site and not the type of mutations. When we looked in more detail at mutations between codons 170-1578 in the 68 patients with attenuated phenotype who did not conform with the expected genotype-phenotype correlation, we observed some distinctive features.
In this patient group there was an unexpectedly high proportion of splice site mutations: 20/68 = 29% in patients with attenuated phenotype vs. 25/587 = 4% in patients with typical phenotype (p < 0.001; Fisher's exact test, two sided). Some of these splice site mutations may lead to in-frame deletions or to partial exon deletions. We present some examples: we showed by RNA analysis that the substitution c.1312+3A>G in intron 9 detected in two unrelated patients with attenuated phenotype leads to partial loss of exon 9, while the substitution at position +5 of this intron (c.1312+5G>A) detected in a family with typical FAP leads to complete loss of exon 9. Moreover, the substitution at the highly conserved position -2 in intron 14 (c.1959-2A>G) is predicted to result in a splicing defect. RNA analysis demonstrated a partial use of a cryptic splice site 12 bp downstream, resulting in a slightly shortened in-frame transcript and likely to lead to a functional APC protein [19].
Somatic mosaicism in patients with de novo mutations may be another reason for an attenuated phenotype. In two patients the nonsense mutations p. Arg216X and p. Gln1127X, respectively, were detected in blood samples only as faint signals, suggesting in these cases the presence of a somatic mosaic in the blood and possibly in the colonic epithelium. In the two patients with the 5 bp deletion at codon 1309 and an attenuated phenotype the mutation had occurred de novo; the mutant alleles were detected in their blood samples at normal levels (comparable to familial cases) but may be present as somatic mosaics in the intestinal epithelium.
While these examples can explain only some of the cases of nonconformity with the established genotype-phenotype correlations, they demonstrate that mutational consequences may be different even if mutations occur in the immediate vicinity of one another. Since the majority of mutations are truncating and most cases of possible mosaicism affect only the first generation, exceptions to the otherwise consistent genotype-phenotype correlations are relatively rare.
Modifier genes
The intrafamilial variability frequently observed in large multigeneration FAP families [41,43-45] cannot be explained by the reasons outlined above. Variations in other genes acting as modifiers at the level of APC synthesis and function or on other regulatory proteins in Wnt signalling and cell adhesion are discussed as causative factors of phenotypic variability within families or in patients with the same germline mutation. In animal experiments a variant in the secretory type II phospholipase A2 gene (Pla2s) designed as MOM1 (modifier of Min) has been proven as the first modifier influencing the number of intestinal polyps in Min mice [46]. Discordant findings regarding the existence of a modifying locus for severity of colonic or extracolonic manifestations in FAP on human chromosome 1p35-36, the region synthenic with the Pla2s locus on mouse chromosome 4, have been published [47-50]. Moreover, polymorphisms in enzymes playing a role in different metabolic and cell cycle controlling pathways, e.g. N-acetyl transferase type 1 and 2, glutathione S-transferases M1 amd T1, and others, have been examined for possible modifying effects on gastrointestinal and extragastrointestinal symptoms [47-50]; however, no concordant results were obtained.
Desmoid disease and osteomas
A higher frequency of desmoid tumours and osteomas has been repeatedly observed in FAP patients with a germline mutation 3' to codon 1444 [8,51]. Moreover, several families with mutations in the 3' part of the APC gene who developed desmoids in the absence of polyposis or with a very mild polyposis phenotype have been described [52,53].
In our patient sample presence or absence of desmoids and osteomas was only occasionally reported in the medical records, and we have not specifically asked for this information during the last few years. Therefore, our data on these extracolonic manifestations are mainly similar to those previously published [28]. The actual data are presented in Table 4. Information on desmoid and osteoma status was obtained from 380 and 195 patients with identified mutations, respectively. From these data it becomes evident that in a retrospective study like ours, where patients are not explicitly examined for desmoids or osteomas, there must be a selection bias: the presence of clinically manifest desmoids or osteomas in patients is more likely to be documented as compared to their absence. Therefore, when calculating the presence of these extracolonic manifestations on the basis of patients with documented disease status, the values are too high. We believe that the proportions calculated on the basis of all patients with mutations in different APC regions (figures given in parentheses in Table 4) better reflect the real situation regarding the presence of these extracolonic features. Even with this rough estimation the higher proportion of desmoids and osteomas in patients with mutations 3' to codon 1444 remains evident. Of note, CHRPE status is not so much affected by this selection bias, because determination of the presence or absence of CHRPE requires a special ophthalmological examination.
Table 4.
Distribution of patients according to the site of APC mutation and the presence or absence of desmoids and osteomas
| Site of mutation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 5' to codon 1444 | 3' to codon 1444 | large deletions | |
| All patients | 1379 | 1169 | 132 | 78 |
| Desmoids | ||||
| present | 76 | 52 | 19 | 5 |
| absent | 304 | 267 | 22 | 15 |
| all* | 380 | 319 | 41 | 20 |
| % desmoids | 20% | 16% | 46% | 25% |
| % desmoids (minimal estimate)** | (5%) | (4%) | (14%) | (6%) |
| Osteomas | ||||
| present | 65 | 36 | 28 | 1 |
| absent | 130 | 115 | 8 | 7 |
| all* | 195 | 151 | 36 | 8 |
| % osteomas | 33% | 23% | 78% | 12% |
| % osteomas (minimal estimate)** | (5%) | (3%) | (21%) | (1%) |
*number of patients with records regarding presence or absence of desmoids/osteomas
**Because of a selection bias towards patients with expressed desmoids or osteomas, a minimal estimate was calculated based on the documented presence of the respective extracolonic manifestations in all patients.
Conclusion
The discovery of the molecular basis of FAP by identification of germline mutations in the APC gene in polyposis patients has stimulated the interest of clinicians and molecular biologists in this disease. During the last years several groups of polyposis patients have been examined for mutations in the APC gene. APC mutation detection rates in FAP patients varying between 30-85% have been published. This variation largely depends on patient selection and their clinical phenotype: the discovery that attenuated FAP is also caused by germline mutations in the APC gene has increased the proportion of patients with few adenomas irrespective of the family history among patients examined for mutations. This has led to an overall decrease in the mutation detection rate. Our data show mutation detection rates up to 85% when patients with typical FAP are considered.
Impressive correlations between the site of mutations in the large APC gene and the clinical phenotype including both the colonic polyposis phenotype and manifestation of extracolonic features have been published. Examination for CHRPE had been proposed as a useful marker for pointing to the gene region that should be examined for APC mutations. In addition, CHRPE status was thought to be used for predictive testing in families with no identified APC mutation, but where the index patient presents with CHRPE. However, findings of intrafamilial discrepancies in CHRPE status limit its use as a predictive marker in persons at risk. Moreover, due to the absence of CHRPE in most patients with an attenuated polyposis phenotype, ophthalmogical examinations are of little value in the actual diagnostic procedure.
The association of attenuated FAP with APC mutations localised in the 5' or 3' part of the gene or in the alternatively spliced region of exon 9 has also repeatedly been published and has been, in principle, confirmed in our sample of 1379 patients with known APC mutations. When examining this correlation it should be kept in mind that classification of the clinical phenotype into typical and attenuated FAP may be difficult in some cases. This classification is based ideally on the age at onset of polyp growth and age-related polyp numbers, but in most cases these data are not available because patients are diagnosed at different stages of disease development. On the other hand, the type of mutation may also play a role and may explain some exceptions to the expected relationship. In addition, even intrafamilial variation of the clinical phenotype has been described, pointing to the presence of other genetic or environmental factors. Therefore, identification of the APC mutation in a patient is of limited value for the prediction of the clinical course of the disease or for therapeutic decisions.
The discovery of MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP) due to biallelic mutations in the MUTYH gene has complicated our perception of adenomatous polyposis. Initially it was thought that all cases of adenomatous polyposis follow an autosomal-dominant mode of inheritance and are caused by mutations in the APC gene, irrespective of whether or not the mutation was identified. The existence of an autosomal-recessive polyposis disease that clinically resembles FAP implies that some statements regarding risk predictions in the families based on indirect genotype analysis or apparent de novo mutations have to be reevaluated. The frequency of MUTYH-associated polyposis among unselected APC-mutation-negative polyposis patients ranges between 15% and 40%.
In this context the search for an APC mutation, especially in patients without a family history of FAP, is of importance for defining the recurrence risk in their families. However, mutation analysis is still laborious and expensive, and even with more up-to-date and sophisticated methods a mutation in the APC (or MUTYH) gene(s) cannot be excluded. Moreover, as other polyposis syndromes (e.g. familial juvenile polyposis or Peutz Jeghers syndrome, caused by mutations in other genes) have to be considered as differential diagnoses, we would like to emphasise the importance of the clinical diagnosis including polyp number, site of location in the colorectum and histology, and family history prior to requesting molecular diagnostics. These data, especially polyp histology, are necessary in order to differentiate between different types of polyposis and to provide mutation analysis of the appropriate genes.
The identification of the underlying germline mutation(s) in polyposis patients allows predictive diagnostics in persons at risk in their families. Genetic counselling should be offered to the patients and their families in order to explain the complex picture of polyposis disease, including the possibilities and limitations of molecular diagnostics for surveillance and therapy.
Supplementary table 1. 315 different point mutations detected in 597 out of 1166 unrelated patients suspected of FAP. (The DNA mutation numbering is based on the cDNA sequence for APC where +1 corresponds to the A of the ATG translation initiation codon in the reference sequence Genbank, NM_000038.2.)
| Exon/Intron | Codon | Mutation | Consequence | Number of alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 122 | c.366delG | p.Gly122fs | 1 |
| 3 | 129 | c.386_387insT | p.Glu129fs | 1 |
| 3 | 139 | c.416_419delAAGA | p.Lys139fs | 1 |
| intron 3 | 141 | c.423-5A>G | 2 | |
| intron 3 | 141 | c.423-3T>A | 1 | |
| intron 3 | 141 | c.423-2A>T | 1 | |
| intron 3 | 141 | c.423-1G>A | 1 | |
| intron 3 | 141 | c.423-1G>T | 1 | |
| intron 3 | 141 | c.423-1G>C | 1 | |
| 4 | 141 | c.423G>T | p.Arg141>Ser* | 2 |
| 4 | 142 | c.426_427delAT | p-Ser142fs | 1 |
| 4 | 150 | c.450_453delAGAA | p.Lys150fs | 2 |
| 4 | 151 | c.453delA | p.Glu151fs | 1 |
| 4 | 152 | c.455_459delAAAAG | p.Glu152fs | 1 |
| 4 | 153 | c.457_458delAA | p.Lys153fs | 1 |
| 4 | 156 | c.468_472delCTGGT | p.Asp156fs | 1 |
| 4 | 159 | c.477C>G | p.Tyr159X | 2 |
| 4 | 161 | c.481C>T | p.Gln161X | 1 |
| 4 | 170 | c.509_512delATAG | p.Asp170fs | 4 |
| 4 | 171 | c.509_512dupATAG | p.Ser171fs | 1 |
| intron 4 | 177 | c.531+1G>A | 1 | |
| intron 4 | 177 | c.531+5G>C | 1 | |
| intron 4 | 177 | c.531+5_531+8delGTAA | 2 | |
| intron 4 | 178 | c.532-2A>G | 1 | |
| intron 4 | 178 | c.532-1G>T | 1 | |
| 5 | 181 | c.540_541insA | 1 | |
| 5 | 181 | c.541C>T | p.Gln181X | 4 |
| 5 | 191 | c.573dupT | p.Tyr191fs | 1 |
| 5 | 197 | c.591_592delAG | p.Arg197fs | 1 |
| 5 | 203 | c.607delC | p.Gln203fs | 2 |
| 5 | 213 | c.637C>T | p.Arg213X | 7 |
| 5 | 214 | c.641dupC | p.Ala214fs | 1 |
| 6 | 216 | c.646C>T | p.Arg216X | 6 |
| 6 | 225 | c.673G>T | p.Glu225X | 1 |
| 6 | 226 | c.677delA | p.Lys226fs | 1 |
| 6 | 232 | c.694C>T | p.Arg232X | 6 |
| 6 | 242 | c.726delA | p.Pro242fs | 1 |
| intron 6 | 243 | c.730-1G>T | 2 | |
| 7 | 264 | c.790C>T | p.Gln264X | 1 |
| 7 | 267 | c.799G>T | p.Gly267X | 1 |
| 7 | 271 | c.812delT | p.Met271fs | 1 |
| 7 | 271 | c.811_818delATGGCAAC | p.Met271fs | 1 |
| 7 | 278 | c.834G>A | p.Gln278 | 1 |
| 8 | 283 | c.847C>T | p.Arg283X | 6 |
| 8 | 297 | c.891_894delACAC | p.Thr297fs | 1 |
| 8 | 302 | c.904C>T | p.Arg302X | 5 |
| intron 8 | 311 | c.933+2T>C | 1 | |
| intron 8 | 311 | c.933+1delG | 1 | |
| 9 | 314 | c.940dupA | p.Met314fs | 1 |
| 9 | 332 | c.994C>T | p.Arg332X | 9 |
| 9 | 340 | c.1018_1019dupTC | p.Ser340fs | 1 |
| 9 | 367 | c.1100_1101delCT | p.Ser367fs | 1 |
| 9 | 368 | c.1102dupG | p.Val368fs | 1 |
| 9 | 374 | c.1120dupC | p.Ar.374fs | 1 |
| 9 | 386 | c.1158_1159delAC | p.Ala386fs | 1 |
| 9 | 398 | c.1192_1193delAA | p.Lys398fs | 2 |
| 9 | 405 | c.1213C>T | p.Arg405X | 3 |
| 9 | 414 | c.1240C>T | p.Arg414Cys | 1 |
| 9 | 414 | c.1242delC | p.Arg414fs | 1 |
| 9 | 423 | c.1269G>A | p.Trp423X | 2 |
| 9 | 433 | c.1297C>T | p.Glu433X | 2 |
| 9 | 436 | c.1307dupA | p.Asn436fs | 1 |
| intron 9 | 438 | c.1312+2dupT | 3 | |
| intron 9 | 438 | c.1312+2T>C | 1 | |
| intron 9 | 438 | c.1312+3A>G; | 2 | |
| intron 9 | 438 | c.1312+5C>A | 1 | |
| 10 | 438 | c.1313dupT | p.Met438fs | 1 |
| 10 | 445 | c.1333_1334dupCA | p.Gln445fs | 1 |
| 10 | 457 | c.1370C>G | p.Ser457X | 2 |
| 10 | 457 | c.1370C>A | p.Ser457X | 2 |
| intron 10 | 470 | c.1409-5A>G | 1 | |
| intron 10 | 470 | c.1409-2A>C | 1 | |
| intron 10 | 470 | c.1409-2A>G | 1 | |
| intron 10 | 470 | c.1409-1G>A | 1 | |
| 11 | 471 | c.1411G>T | p.Gly471X | 1 |
| 11 | 471 | c.1412delG | p.Gly471fs | 1 |
| 11 | 473 | c.1417delC | p.Gln473fs | 1 |
| 11 | 478 | c.1434delA | p.Ile478fs | 1 |
| 11 | 493 | c.1479_1483delCAGTA | p.Tyr493fs | 1 |
| 11 | 499 | c.1495C>T | p.Arg499X | 8 |
| 11 | 516 | c.1548G>C | p.Lys516Asn | 1 |
| 12 | 517 | c.1549-1G>A | 1 | |
| 12 | 519 | c.1555dupC | p.Leu519fs | 1 |
| 12 | 527 | c.1581_1590del10bp | p.Arg527fs | 1 |
| 12 | 528 | c.1584dupA | p.Ala528fs | 2 |
| 12 | 538 | c.1613A>T | p.Glu538Val | 1 |
| 12 | 541 | c.1621C>T | p.Gln541X | 1 |
| 12 | 542 | c.1624C>T | p.Gln542X | 1 |
| 13 | 554 | c.1660 C>T | p.Arg554X | 10 |
| 13 | 561 | c.1683_1684delGA | p.Lys561fs | 1 |
| 13 | 562 | c.1685_1686insCC | p.Thr562fs | 1 |
| 13 | 563 | c.1688delT | p.Leu563fs | 1 |
| 13 | 564 | c.1690C>T | p.Arg564X | 9 |
| 13 | 567 | c.1700_1704delGAAGT | p.Gly567fs | 1 |
| 13 | 571 | c.1712delC | p.Ala571fs | 1 |
| 13 | 580 | c.1737dupT | p.Lys580fs | 1 |
| 13 | 581 | c.1742delA | p.Lys581fs | 1 |
| 13 | 581 | c.1742A>G | p.Lys581Arg | 1 |
| intron 13 | 582 | c.1744-2A>G | 1 | |
| intron 13 | 582 | c.1744-[5_13del; 17_18del] | 1 | |
| 14 | 583 | c.1748C>A | p.Ser583X | 1 |
| 14 | 592 | c.1775T>G | p.Leu592X | 1 |
| 14 | 593 | c.1779G>A | p.Trp593X | 1 |
| 14 | 599 | c.1797C>A | p.Cys599X | 1 |
| 14 | 614 | c.1840dupG | p.Gly614fs | 2 |
| 14 | 616 | c.1847delT | p.Leu616fs | 1 |
| 14 | 617 | c.1849delG | p.Val617fs | 1 |
| 14 | 620 | c.1858_1859dupCT | p.Leu620fs | 3 |
| 14 | 621 | c.1861dupA | p.Thr621fs | 1 |
| 14 | 621 | c.1863_1866delTTAC | p.Thr621fs | 3 |
| 14 | 622 | c.1866C>G | p.Tyr622X | 1 |
| 14 | 628 | c.1884_1897dup14 | p.Thr628fs | 1 |
| 14 | 629 | c.1886delT | p.Leu629fs | 1 |
| 14 | 629 | c.1886dupT | p.Leu629fs | 1 |
| 14 | 629 | c.1885_1886dupTT | p.Leu629fs | 1 |
| 14 | 630 | c.1890delC | p.Ala630fs | 1 |
| 14 | 636 | c.1907dupG | p.Gly636fs | 1 |
| 14 | 639 | c.1916delT | p.Leu639fs | 2 |
| 14 | 650 | c.1948G>T | p.Glu650X | 1 |
| 14 | 652 | c.1956C>T | p.His652* | 1 |
| 14 | 653 | c.1957A>C | p.Arg653* | 2 |
| 14 | 653 | c.1957A>G | p.Arg653Gly* | 1 |
| intron 14 | 653 | c.1958+1G>T | 4 | |
| intron 14 | 653 | c.1958+1G>A | 1 | |
| intron 14 | 653 | c.1958+3A>G | 2 | |
| intron 14 | 653 | c.1959-2A>G | 1 | |
| 15A | 653 | 15A: c.1959delG | 1 | |
| 15A | 658 | c.1972G>T | p.Glu658X | 1 |
| 15A | 669 | c.2005_6delTT | p.Leu669fs | 1 |
| 15A | 685 | c.2055G>A | p.Trp685X | 1 |
| 15A | 703 | c.2107delG | p.Ala703fs | 2 |
| 15A | 703 | c.2107dupG | p.Ala703fs | 1 |
| 15a | 710 | c.2130delC | p.Leu710fs | 1 |
| 15A | 712 | c.2136_2139delTTCA | p.His712fs | 1 |
| 15A | 737 | c.2209_2218del10 | p.Tyr737fs | 1 |
| 15A | 747 | c.2240C>G | p.Ser747X | 2 |
| 15B | 757 | c.2269delC | p.Gln757fs | 1 |
| 15B | 767 | c.2299C>T | p.Gln767X | 3 |
| 15B | 770 | c.2309delC | p.Gln770fs | 1 |
| 15B | 773 | c.2318_ 2319delTT | p.Phe773fs | 2 |
| 15B | 779 | c.2335_2336dupTT | p.Leu779fs | 2 |
| 15B | 781 | c.2343delC | p.Pro781fs | 1 |
| 15B | 791 | c.2373_2374delCA | p.Lys791fs | 2 |
| 15B | 797 | c.2391_2392delTG | p.Gly797fs | 1 |
| 15B | 799 | c.2396_2397delAT | p.Tyr799fs | 1 |
| 15B | 805 | c.2413 C>T | p.Arg805X | 3 |
| 15B | 811 | c.2432C>G | p.Ser811X | 1 |
| 15B | 828 | c.2483delC | p.Thr828fs | 1 |
| 15B | 834 | c.2502delC | p.Ser834fs | 1 |
| 15C | 837 | c.2510delC | p.Ser837fs | 1 |
| 15C | 841 | c.2523dupA | p.Leu841fs | 1 |
| 15C | 843 | c.2527_2530delAGTT | p.Ser843fs | 1 |
| 15C | 849 | c.2547_2548delTA | p.Asp849fs | 1 |
| 15C | 849 | c.2546_delATAGAAG | p.Asp849fs | 1 |
| 15C | 849 | c.2547_2550delTAGA | p.Asp849fs | 2 |
| 15C | 850 | c.2548delAGAA | p.Arg850fs | 1 |
| 15C | 855 | c.2563G>T | p.Glu855X | 1 |
| 15C | 855 | c.2563_2564delGA | p.Glu855fs | 1 |
| 15C | 857 | c.2570delG | p.Gly857fs | 1 |
| 15C | 863 | c.2589C>G | p.Tyr863X | 1 |
| 15C | 871 | c.2612delG | p.Gly871fs | 1 |
| 15C | 872 | c.2614_2617delACTT | p.Thr872fs | 1 |
| 15C | 876 | c.2626C>T | p.Arg876X | 6 |
| 15C | 900 | c.2698_2699insTG | p.Ser900fs | 1 |
| 15C | 903 | c.2709_2712delCAGA | p.Asp903fs | 1 |
| 15C | 916 | c.2748delA | p.Thr916fs | 1 |
| 15C | 929 | c.2787_2790delTACA | p.His929fs | 1 |
| 15C | 932 | c.2795C>G | p.Ser932X | 1 |
| 15C | 934 | c.2802_2805delTTAC | p.Thr934fs | 3 |
| 15C | 935 | c.2805C>G | p.Tyr935X | 6 |
| 15D | 939 | c.2816delA | p.Lys939fs | 1 |
| 15D | 947 | c.2840delG | p.Cys947fs | 1 |
| 15D | 951 | c.2853T>A | p.Tyr951X | 1 |
| 15D | 951 | c.2853 T>G | p.Tyr951X | 1 |
| 15D | 962 | c.2884delG | p.Asp962fs | 1 |
| 15D | 965 | c.2893_2896delAATA | p.Asn964fs | 3 |
| 15D | 974 | c.2921delG | p.Gly974fs | 1 |
| 15D | 976 | c.2926delA | p.Arg976fs | 1 |
| 15D | 978 | c.2932C>T | p.Gln978X | 2 |
| 15D | 985 | c.2953_3022del70 | p.Ser985fs | 1 |
| 15D | 985 | c.2953dupT | p.Ser985fs | 1 |
| 15D | 997 | c.2991T>G | p.Tyr997X | 1 |
| 15D | 1000 | c.3000C>G | p.Tyr100X | 1 |
| 15D | 1010 | c.3027_3028dupTA | p.Ser1010fs | 1 |
| 15D | 1023 | c.3068delC | p.Thr1023fs | 1 |
| 15D | 1023 | c.3069_3070delAC | p.Thr1023fs | 1 |
| 15D | 1024 | c.3071delC | p.Pro1027fs | 1 |
| 15D | 1032 | c.3095C>A | p.Ser1032X | 1 |
| 15D | 1041 | c.3121C>T | p.Gln1041X | 2 |
| 15E | 1044 | c.3131C>A | p.Ser1044X | 1 |
| 15E | 1045 | c.3133C>T | p.Gln1045X | 1 |
| 15E | 1049 | c.3146G>A | p.Trp1049X | 1 |
| 15E | 1049 | c.3147G>A | p.Trp1049X | 1 |
| 15E | 1050 | c.3148delG | p.Ala1050fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1050 | c.3149delC | p.Ala1050fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1055 | c.3164_3168delTAATA | p.Ile1055fs | 4 |
| 15E | 1055 | c.3164_3165delTA | p.Ile1055fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1061 | c.3183_3187delACAAA | p.Lys1061fs | 43 |
| 15E | 1062 | c.3184_3187delCAAA | p.Gln1062fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1062 | c.3186_3187delAA | p.Gln1062fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1065 | c.3193C>T | p.Gln1965X | 1 |
| 15E | 1068 | c.3202_3205delTCAA | p.Ser1068fs | 19 |
| 15E | 1071 | c.3211C>T | p.Gln1071X | 1 |
| 15E | 1072 | c.3215_3216delGTinsC | p.Ser1072fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1075 | c.3225delT | p.Tyr1075fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1087 | c.3260_3261delTC | p.Leu1087fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1088 | c.3263delA | p.Gln1088fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1096 | c.3286C>T | p.Gln1096X | 3 |
| 15E | 1107 | c.3316_3319dupGGAG | p.Ala1107fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1114 | c.3340C>T | p.Arg1114X | 5 |
| 15E | 1121 | c.3361delA | p.Glu1121fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1127 | c.3379C>T | p.Gln1127X | 1 |
| 15E | 1129 | c.3386T>C | p.Leu1129Ser | 1 |
| 15E | 1130 | c.3390T>A | p.Cys1130X | 1 |
| 15E | 1132 | c.3394delG | p.Glu1132fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1147 | c.3439dupT | p.Tyr1147fs | 1 |
| 15E | 1147 | c.3441C>G | p.Tyr1147X | 1 |
| 15E | 1152 | c.3454C>T | p.Gln1152X | 1 |
| 15E | 1155 | c.3464_3468delAAGAA | p.Glu1155fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1156 | c.3467_3470delAAGA | p.Glu1156fs | 4 |
| 15F | 1157 | c.3471_3474delGAGA | p.Glu1157fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1166 | c.3497dupA | p.Tyr1166fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1167 | c.3501_3504delTGAA | p.Asn1167fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1168 | c.3502G>T | p.Glu1168X | 2 |
| 15F | 1169 | c.3505_3509delGAGAA | p.Glu1169fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1186 | c.3556_3557 delGA | p.Asp1186fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1187 | c.3559dupA | p.Ile1187fs | 2 |
| 15F | 1193 | c.3577_3578delCA | p.Gln1193fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1194 | c.3581C>A | p.Ser1194X | 1 |
| 15F | 1194 | c.3581C>G | p.Ser1194X | 1 |
| 15F | 1196 | c.3587C>A | p.Ser1196X | 1 |
| 15F | 1198 | c.3593C>G | p.Ser1198X | 1 |
| 15F | 1199 | c.3595_3596delAA | p.Lys1199fs | 4 |
| 15F | 1201 | c.3602C>G | p.Ser1201X | 1 |
| 15F | 1209 | c.3625_3628delGAAC | p.Glu1209fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1222 | c.3666_3679del14 | p.Ser1222fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1230 | c.3688C>T | p.Gln1230X | 1 |
| 15F | 1244 | c.3730C>T | p.Gln1244X | 1 |
| 15F | 1249 | c.3747C>A | p.Cys1249X | 1 |
| 15F | 1250 | c.3749_3750delAA | p.Lys1250fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1256 | c.3768dupA | p.Glu1257fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1262 | c.3786T>A | p.Tyr1262X | 1 |
| 15F | 1267 | c.3796_3799dupGATA | p.Thr1267fs | 2 |
| 15F | 1268 | c.3803_3815del13 | p.Pro1268fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1269 | c.3805delA | p.Ile1269fs | 1 |
| 15F | 1269 | c.3806dupT | p.Ile1269fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1270 | c.3810_3811insC | p.Phe1270fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1272 | c.3816_3817ins14 | p.Arg1272fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1275 | c.3824_3831delGTTCATTA | p.Ser1275fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1278 | c.3833C>A | p.Ser1278X | 1 |
| 15G | 1286 | c.3856G>T | p.Glu1286X | 1 |
| 15G | 1294 | c.3880delC | p.Gln1294fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1298 | c.3892_3903del12insATTT | p.Ser1298fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1309 | c.3925G>T | p.Glu1309X | 2 |
| 15G | 1309 | c.3925-3928delGAAA | p.Glu1309fs | 5 |
| 15G | 1309 | c.3927_3931delAAAGA | p.Glu1309fs | 56 |
| 15G | 1321 | c.3963delC | p.Ser1321fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1338 | c.4012C>T | p.Gln1338X | 1 |
| 15G | 1341 | c.4022delG | p.Ser1341fs | 1 |
| 15G | 1341 | c.4022_4023ins22 | p.Ser1341fs | 2 |
| 15G | 1342 | c.4025dupT | p.Leu1342fs | 2 |
| 15G | 1344 | c.4031C>G | p.Ser1344X | 1 |
| 15H | 1367 | c.4099C>T | p.Gln1367X | 2 |
| 15H | 1376 | c.4128delT | p.Tyr1376fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1376 | c.4127_4128delAT | p.Tyr1376fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1378 | c.4132C>T | p.Gln1378X | 1 |
| 15H | 1381 | c.4142dupC | p.His1381fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1400 | c.4199C>A | p.Ser1400X | 1 |
| 15H | 1425 | c.4273delGA | p.Asp1425fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1426 | c.4275dupT | p.Ser1426fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1432 | c.4295delC | p.Pro1432fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1444 | c.4331C>T | p.Gln1444X | 1 |
| 15H | 1450 | c.4348C>T | p.Arg1450X | 5 |
| 15H | 1451 | c.4351G>T | p.Glu1451X | 1 |
| 15H | 1455 | c.4364_4368delATAAA | p.Asn1455fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1459 | c.4377delT | p.Thr1459fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1461 | c.4383_4387delAAAGA | p.Lys1461fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1462 | c.4385delA | p.Arg1462fs | 1 |
| 15H | 1464 | c.4391_4394delAGAG | p.Glu1464fs | 3 |
| 15H | 1465 | c.4393_4394delAG | p.Ser1465fs | 8 |
| 15I | 1495 | c.4483delA | p.Ser1495fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1496 | c.4487dupC | p.Thr1496fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1498 | c.4492del G | p.Asp1498fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1516 | c.4547_4548delTA | p.p.Ile1516fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1517 | c.4549C>G | p.Gln1517X | 2 |
| 15I | 1522 | c.4570_4576del7 | p.Ile1522fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1531 | c.4592dupA | p.Met1531fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1538 | c.4612_4613delGA | p.Glu1538fs | 2 |
| 15I | 1541 | c.4621C>T | p.Gln1541X | 1 |
| 15I | 1545 | c.4634C>G | p.Ser1545X | 1 |
| 15I | 1548 | c.4643delA | p.Asn1548fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1551 | c.4652_4655delAAGA | p.Lys1551fs | 2 |
| 15I | 1556 | c.4666delA | p.Thr1556fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1556 | c.4666dupA | p.Thr1556fs | 3 |
| 15I | 1563 | c.4688_4703del16 | p.Leu1563fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1565 | c.4694T>A | p.Leu1565X | 1 |
| 15I | 1567 | c.4700C>G | p.Ser1567X | 1 |
| 15I | 1578 | c.4733_4734delGT | p.Cys1578fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1581 | c.4741dupT | p.Leu1581fs | 1 |
| 15I | 1596 | c.4786delC | p.Gln1596fs | 4 |
| 15I | 1600 | c.4799_4800dupAA | p.Asn1600fs | 1 |
| 15J | 1628 | c.4883delA | p.Lys1628fs | 1 |
| 15J | 1652 | c.4954delT | p.Ser1652fs | 1 |
| 15J | 1661 | c.4982_4983insTA | p.Thr1661fs | 1 |
| 15J | 1683 | c.5047G>T | p.Glu1683X | 1 |
| 15L | 1823 | c.5471delA | p.Asn1823fs | 1 |
| 15N | 1958 | c.5873delA | p.Asn1958fs | 2 |
| 15N | 1973 | c.5917delA | p.Ser1973fs | 1 |
| 15N | 1981 | c.5943_5946delTAAA | p.Ile1981fs | 1 |
| 15M | 1983 | c.5947_5950delGAAA | p.Glu1983fs | 1 |
| 15N | 1984 | c.5952_5955delTGAA | p.Asn1984fs | 1 |
| 15N | 1986 | c.5957delC | p.Pro1986fs | 1 |
| 15N | 1993 | c.5978delC | p.Pro1993fs | 1 |
| 15P | 2117 | c.6351delA | p.Gln2117fs | 1 |
| 15P | 2192 | c.6574A>T | p.Lys2192X | 1 |
| 15T | 2557 | c.7671_7678delCCTTCCTC | p.Ser2557fs | 1 |
*These missense or silent mutations result in exon splicing [19]
Supplementary table 2. Large deletions detected in 37 out of 1166 unrelated patients suspected of FAP
| Deleted exons | Genomic deletion GenBank AC008575.7 | Number of alleles |
|---|---|---|
| Cytogenetic deletion | cytogenic | 1 |
| Promotor and whole gene | g.26940-?_133343+?del | 16 |
| Promotor and exon 1 | g.26940-?_44326+?del | 1 |
| Promotor and exon 1-5 | g.26940-?_70201+?del | 1 |
| Promotor and exon 1-7 | g.26940-?_90721+?del | 1 |
| Promotor and exon 1-10 | g.26940-?_111301+?del | 1 |
| Exon 1-15 end | g.44326-?_133343+?del | 2 |
| Exon 2-15 end | g.55780-?_133343+?del | 1 |
| Exon 4 | g.65700-?_66200+?del | 1 |
| Exon 5-15 end | g.70201-?_133343+?del | 1 |
| Exon 8-15 end | g.104881-?_133343+?del | 1 |
| Exon 9-15 end | g.108601-?_133343+?del | 1 |
| Exon 11 | g.115000-?_116900+?del | 1 |
| Exon 11-12 | g.116521-?_1117361+?del | 2 |
| Exon 11-15 end | g.116521-?_133343+?del | 1 |
| Exon 14 | g.123900-?_125100+?del | 2 |
| Exon 14-15 middle | g.123900-?_129830+?del | 1 |
| Exon 14-15 end | g.123900-?_133343+?del | 1 |
| Exon 15 middle - 15 end | g.129830-?_133343+?del | 1 |
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patients who participated in the study and to the colleagues who helped us with clinical information about the patients. We thank K. Siberg and M. Vogel for data collection and M. Sengteller, D. Stienen and S. Uhlhaas for skilful technical assistance. The study was supported by German Cancer Aid (Deutsche Krebshilfe e. V. Bonn, project no. 106244).
References
- Bülow S. Clinical features in familial polyposis coli. Results of the Danish Polyposis Register. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986;29(2):102–107. doi: 10.1007/BF02555389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, Albertsen H, Joslyn G, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, Sargeant L, Krapcho K, Wolff E, Burt R, Hughes JP, Warrington J, McPherson J, Wasmuth J, Le Paslier D, Abderrahim H, Cohen D, Leppert M, White R. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler KW, Nilbert MC, Su LK, Vogelstein B, Bryan TM, Levy DB, Smith KJ, Preisinger AC, Hedge P, McKechnie D, Finniear R, Markham A, Groffen J, Boguski MS, Altschul SF, Horii A, Ando H, Miyoshi Y, Miki Y, Nishisho I, Nakamura Y. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss KH, Groden J. Biology of the adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(9):1967–1979. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.9.1967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodde R, Smits R, Clevers H. APC, signal transduction and genetic instability in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1(1):55–67. doi: 10.1038/35094067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirio L, Olschwang S, Groden J, Robertson M, Samowitz W, Joslyn G, Gelbert L, Thliveris A, Carlson M, Otterud B, Lynch H, Watson P, Lynch P, Laurent Puig P, Burt R, Hughes JP, Thomas G, Leppert M, White R. Alleles of the APC gene: an attenuated form of familial polyposis. Cell. 1993;75(5):951–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R, Friedl W, Mandl M, Moslein G, Kadmon M, Knapp M, Jacobasch KH, Ecker KW, Kreissler-Haag D, Timmermanns G, Propping P. Familial adenomatous polyposis: mutation at codon 1309 and early onset of colon cancer. Lancet. 1994;343(8898):629–632. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)92634-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R, Olschwang S, Friedl W, Mandl M, Boisson C, Boker T, Augustin A, Kadmon M, Möslein G, Thomas G, Propping P. Familial adenomatous polyposis: desmoid tumours and lack of ophthalmic lesions (CHRPE) associated with APC mutations beyond codon 1444. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4(3):337–340. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschwang S, Tiret A, Laurent-Puig P, Muleris M, Parc R, Thomas G. Restriction of ocular fundus lesions to a specific subgroup of APC mutations in adenomatous polyposis coli patients. Cell. 1993;75(5):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis YL, Macdonald F, Hulten M, Morton JE, McKeown CM, Neoptolemos JP, Keighley M, Morton DG. Genotype-phenotype correlation between position of constitutional APC gene mutation and CHRPE expression in familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Genet. 1994;94(5):543–548. doi: 10.1007/BF00211023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soravia C, Berk T, Madlensky L, Mitri A, Cheng H, Gallinger S, Cohen Z, Bapat B. Genotype-phenotype correlations in attenuated adenomatous polyposis coli. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;62(6):1290–1301. doi: 10.1086/301883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H, Miyoshi Y, Horii A, Aoki T, Ogawa M, Utsunomiya J, Baba S, Sasazuki T, Nakamura Y. Correlation between the location of germ-line mutations in the APC gene and the number of colorectal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Cancer Res. 1992;52(14):4055–4057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tassan N, Chmiel NH, Maynard J, Fleming N, Livingston AL, Williams GT, Hodges AK, Davies DR, David SS, Sampson JR, Cheadle JP. Inherited variants of MYH associated with somatic G: C-->T: A mutations in colorectal tumors. Nat Genet. 2002;30(2):227–232. doi: 10.1038/ng828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isidro G, Laranjeira F, Pires A, Leite J, Regateiro F, Castro e Sousa F, Soares J, Castro C, Giria J, Brito MJ, Medeira A, Teixeira R, Morna H, Gaspar I, Marinho C, Jorge R, Brehm A, Ramos JS, Boavida MG. Germline MUTYH (MYH) mutations in Portuguese individuals with multiple colorectal adenomas. Hum Mutat. 2004;24(4):353–354. doi: 10.1002/humu.9282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson JR, Dolwani S, Jones S, Eccles D, Ellis A, Evans DG, Frayling I, Jordan S, Maher ER, Mak T, Maynard J, Pigatto F, Shaw J, Cheadle JP. Autosomal recessive colorectal adenomatous polyposis due to inherited mutations of MYH. Lancet. 2003;362(9377):39–41. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieber OM, Lipton L, Crabtree M, Heinimann K, Fidalgo P, Phillips RK, Bisgaard ML, Orntoft TF, Aaltonen LA, Hodgson SV, Thomas HJ, Tomlinson IP. Multiple colorectal adenomas, classic adenomatous polyposis, and germ-line mutations in MYH. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(9):791–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa025283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aretz S, Uhlhaas S, Caspari R, Mangold E, Pagenstecher C, Propping P, Friedl W. Frequency and parental origin of de novo APC mutations in familial adenomatous polyposis. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004;12(1):52–58. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luijt R van der, Khan PM, Vasen H, van Leeuwen C, Tops C, Roest P, den Dunnen J, Fodde R. Rapid detection of translation-terminating mutations at the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene by direct protein truncation test. Genomics. 1994;20(1):1–4. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aretz S, Uhlhaas S, Sun Y, Pagenstecher C, Mangold E, Caspari R, Moslein G, Schulmann K, Propping P, Friedl W. Familial adenomatous polyposis: aberrant splicing due to missense or silent mutations in the APC gene. Hum Mutat. 2004;24(5):370–380. doi: 10.1002/humu.20087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aretz S, Stienen D, Uhlhaas S, Pagenstecher C, Mangold E, Caspari R, Propping P, Friedl W. Large submicroscopic genomic APC deletions are a common cause of typical familial adenomatous polyposis. J Med Genet. 2005;42(2):185–192. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2004.022822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl M, Caspari R, Jauch A, Boker T, Raschke H, Sengteller M, Propping P, Friedl W. Familial adenomatous polyposis: a submicroscopic deletion at the APC locus in a family with mentally normal patients. Hum Genet. 1996;97(2):204–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02265266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedle J, Friedl W, Engels H, Koenig R, Trojan J, Zeuzem S. A de novo deletion of chromosome 5q causing familial adenomatous polyposis, dysmorphic features, and mild mental retardation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(10):3016–3020. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.04674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X, Eu KW, Seow-Choen F, Zao Y, Cheah PY. APC mutation and phenotypic spectrum of Singapore familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Eur J Hum Genet. 2000;8(1):42–48. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grobbelaar JJ, Oosthuizen CJ, Kotze MJ. Screening South African familial adenomatous polyposis families for the five-nucleotide deletion at codon 1309 of the APC gene. Mol Cell Probes. 1995;9(1):49–51. doi: 10.1016/S0890-8508(95)91007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaki M, Konishi M, Kikuchi-Yanoshita R, Enomoto M, Igari T, Tanaka K, Muraoka M, Takahashi H, Amada Y, Fukayama M, Maeda Y, Iwama T, Mishima Y, Mori T, Koike M. Characteristics of somatic mutation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene in colorectal tumors. Cancer Res. 1994;54(11):3011–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinimann K, Mullhaupt B, Weber W, Attenhofer M, Scott RJ, Fried M, Martinoli S, Muller H, Dobbie Z. Phenotypic differences in familial adenomatous polyposis based on APC gene mutation status. Gut. 1998;43(5):675–679. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giarola M, Stagi L, Presciuttini S, Mondini P, Radice MT, Sala P, Pierotti MA, Bertario L, Radice P. Screening for mutations of the APC gene in 66 Italian familial adenomatous polyposis patients: evidence for phenotypic differences in cases with and without identified mutation. Hum Mutat. 1999;13(2):116–123. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1999)13:2<116::AID-HUMU3>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl W, Caspari R, Sengteller M, Uhlhaas S, Lamberti C, Jungck M, Kadmon M, Wolf M, Fahnenstich J, Gebert J, Moslein G, Mangold E, Propping P. Can APC mutation analysis contribute to therapeutic decisions in familial adenomatous polyposis? Experience from 680 FAP families. Gut. 2001;48(4):515–521. doi: 10.1136/gut.48.4.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis YL, Morton DG, McKeown CM, Macdonald F. Molecular analysis of the APC gene in 205 families: extended genotype-phenotype correlations in FAP and evidence for the role of APC amino acid changes in colorectal cancer predisposition. J Med Genet. 1999;36(1):14–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott RJ, Meldrum C, Crooks R, Spigelman AD, Kirk J, Tucker K, Koorey D. Hunter Family Cancer Service. Familial adenomatous polyposis: more evidence for disease diversity and genetic heterogeneity. Gut. 2001;48(4):508–514. doi: 10.1136/gut.48.4.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Ponte C, Vega A, Carracedo A, Barros F. Mutation analysis of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene in northwest Spanish patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and sporadic colorectal cancer. Hum Mutat. 2001;18(4):355. doi: 10.1002/humu.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luijt RB van der, Khan PM, Vasen HF, Tops CM, van Leeuwen-Cornelisse IS, Wijnen JT, Klift HM van der, Plug RJ, Griffioen G, Fodde R. Molecular analysis of the APC gene in 105 Dutch kindreds with familial adenomatous polyposis: 67 germline mutations identified by DGGE, PTT, and southern analysis. Hum Mutat. 1997;9(1):7–16. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1997)9:1<7::AID-HUMU2>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies DR, Armstrong JG, Thakker N, Horner K, Guy SP, Clancy T, Sloan P, Blair V, Dodd C, Warnes TW, Harris R, Evans DGR. Severe Gardner syndrome in families with mutations restricted to a specific region of the APC gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1995;57(5):1151–1158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pack K, Smith-Ravin I, Phillips RK, Hodgson SV. Exceptions to the rule: individuals with FAP specific CHRPE and mutations in exon 6 of the APC gene. Clin Genet. 1996;50(2):110–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R, Friedl W, Boker T, Augustin A, Mandl M, Jaeger K, Gallkowski K, Propping P. Predictive diagnosis in familial adenomatous polyposis: evaluation of molecular genetic and ophthalmologic methods. Z Gastroenterol. 1993;31(11):646–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebert JF, Dupon C, Kadmon M, Hahn M, Herfarth C, von Knebel Doeberitz M, Schackert HK. Combined molecular and clinical approaches for the identification of families with familial adenomatous polyposis coli. Ann Surg. 1999;229(3):350–361. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199903000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curia MC, Esposito DL, Aceto G, Palmirotta R, Crognale S, Valanzano R, Ficari F, Tonelli F, Battista P, Mariani-Costantini R, Cama A. Transcript dosage effect in familial adenomatous polyposis: model offered by two kindreds with exon 9 APC gene mutations. Hum Mutat. 1998;11(3):197–201. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1998)11:3<197::AID-HUMU3>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunyan DJ, Shea-Simonds J, Reck AC, Finnis D, Eccles DM. Genotype-phenotype correlations of new causative APC gene mutations in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. J Med Genet. 1995;32(9):728–731. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.9.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luijt RB van der, Vasen HF, Tops CM, Breukel C, Fodde R, Meera Khan P. APC mutation in the alternatively spliced region of exon 9 associated with late onset familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Genet. 1995;96(6):705–710. doi: 10.1007/BF00210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl W, Meuschel S, Caspari R, Lamberti C, Krieger S, Sengteller M, Propping P. Attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis due to a mutation in the 3' part of the APC gene. A clue for understanding the function of the APC protein. Hum Genet. 1996;97(5):579–584. doi: 10.1007/BF02281864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott RJ, Luijt R van der, Spycher M, Mary JL, Muller A, Hoppeler T, Haner M, Muller HJ, Martinoli S, Brazzola PL, Meera Khan P. Novel germline APC gene mutation in a large familial adenomatous polyposis kindred displaying variable phenotypes. Gut. 1995;36(5):731–736. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luijt RB van der, Meera Khan P, Vasen HF, Breukel C, Tops CM, Scott RJ, Fodde R. Germline mutations in the 3' part of APC exon 15 do not result in truncated proteins and are associated with attenuated adenomatous polyposis coli. Hum Genet. 1996;98(6):727–734. doi: 10.1007/s004390050293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brensinger JD, Laken SJ, Luce MC, Powell SM, Vance GH, Ahnen DJ, Petersen GM, Hamilton SR, Giardiello FM. Variable phenotype of familial adenomatous polyposis in pedigrees with 3' mutation in the APC gene. Gut. 1998;43(4):548–552. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello FM, Krush AJ, Petersen GM, Booker SV, Kerr M, Tong LL, Hamilton SR. Phenotypic variability of familial adenomatous polyposis in 11 unrelated families with identical APC gene mutation. Gastroenterology. 1994;106(6):1542–1547. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen P, Samuel Z, Shomrat R, Legum C. Notable intrafamilial phenotypic variability in a kindred with familial adenomatous polyposis and an APC mutation in exon 9. Gut. 1999;45(6):829–833. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee M, Chepenik KP, Liddell RA, Nelson KK, Siracusa LD, Buchberg AM. The secretory phospholipase A2 gene is a candidate for the Mom1 locus, a major modifier of ApcMin-induced intestinal neoplasia. Cell. 1995;81(6):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie Z, Heinimann K, Bishop DT, Muller H, Scott RJ. Identification of a modifier gene locus on chromosome 1p35-36 in familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Genet. 1997;99(5):653–657. doi: 10.1007/s004390050423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasilova M, Russell AM, Wanner A, Wolf A, Dobbie Z, Muller HJ, Heinimann K. Exclusion of an extracolonic disease modifier locus on chromosome 1p33-36 in a large Swiss familial adenomatous polyposis kindred. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004;12(5):365–371. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson IP, Beck NE, Neale K, Bodmer WF. Variants at the secretory phospholipase A2 (PLA2G2A) locus: analysis of associations with familial adenomatous polyposis and sporadic colorectal tumours. Ann Hum Genet. 1996;60(Pt 5):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1996.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson IP, Neale K, Talbot IC, Spigelman AD, Williams CB, Phillips RK, Bodmer WF. A modifying locus for familial adenomatous polyposis may be present on chromosome 1p35-p36. J Med Genet. 1996;33(4):268–273. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.4.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark SK, Phillips RK. Desmoids in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg. 1996;83(11):1494–1504. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800831105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles DM, Luijt R van der, Breukel C, Bullman H, Bunyan D, Fisher A, Barber J, du Boulay C, Primrose J, Burn J, Fodde R. Hereditary desmoid disease due to a frameshift mutation at codon 1924 of the APC gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;59(6):1193–1201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott RJ, Froggatt NJ, Trembath RC, Evans DG, Hodgson SV, Maher ER. Familial infiltrative fibromatosis (desmoid tumours) (MIM135290) caused by a recurrent 3' APC gene mutation. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5(12):1921–1924. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.12.1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]