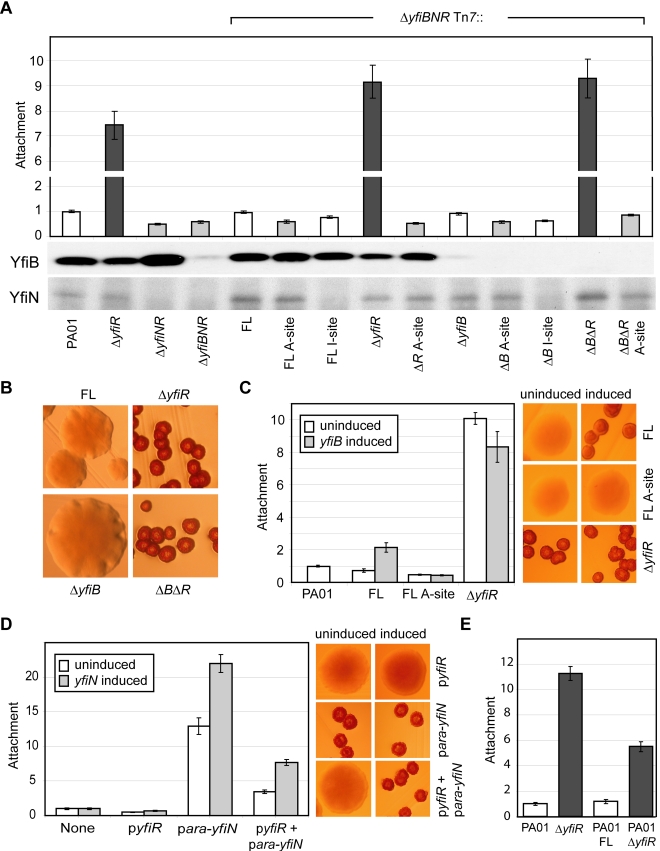
Figure 3. Epistasis and regulation of the YfiBNR system.
A) Attachment of yfiBNR mutant strains. The bars marked ‘ΔyfiBNR Tn7::’ depict Tn7 complementation strains containing variants of the yfiBNR operon inserted into the att-Tn7 site of ΔyfiBNR. For these, ‘FL’ refers to the full-length yfiBNR operon, ‘A-site’ refers to the yfiN active-site mutant D330A, and ‘I site’ to the yfiN feedback-inhibition-site mutant R319A. Strains without an active copy of yfiN (light grey) display reduced attachment compared to those containing active copies of both yfiN and yfiR (white). Strains missing yfiR but containing yfiN (dark grey) showed a large increase in attachment. Immunoblots show the levels of YfiB and YfiN present in each strain. B) Colony morphology of selected Tn7 complementation strains. Deletion of yfiR induces a small colony variant phenotype. Deletion of yfiB has no effect on morphology, either alone or combined with an yfiR deletion. C) Over-expression of yfiB in trans induces SCV colony morphology and stimulates PA01 attachment in an yfiN- and yfiR-dependent manner. yfiB expression is induced in Tn7 complementation strains, which are labeled as in 3A. The colony morphologies of these strains with and without induction of yfiB expression are shown on the right. D) YfiR and YfiN expressed in trans act antagonistically on PA01 colony morphology and attachment. The X-axis of the graph shows the plasmids present in each case. Colony morphologies with and without induction of yfiN expression are shown on the right. E) The full-length yfiBNR operon (FL) and ΔyfiR Tn7 complementation constructs were inserted into the att-Tn7 site of PA01. Attachment levels for all assays are shown relative to PA01.