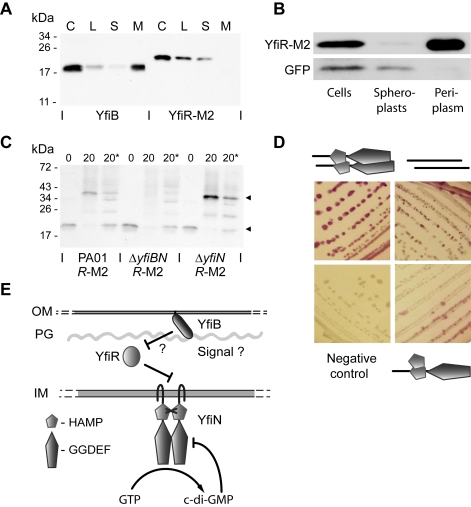
Figure 4. The YfiBNR complex.
A) Membrane localization of YfiB and YfiR. Membrane fractionation was carried out with PA01 yfiR-M2. The separate fractions are labeled as follows: C = whole cell sample, L = cell lysate, S = soluble fraction, M = membrane fraction. YfiB localizes to the membrane fraction, YfiR-M2 to the soluble fraction. B) Periplasmic localization of YfiR. Periplasmic fractionation was carried out with PA01 yfiR-M2 pAD6Ω, and YfiR-M2 and GFP were detected by immunoblot analysis. GFP localizes to the spheroplast (cytosolic/membrane) fraction, while YfiR-M2 localizes to the periplasmic fraction. C) In-vivo crosslinking of YfiR-M2. Whole cell samples of PA01 yfiR-M2, ΔyfiN yfiR-M2, and ΔyfiBN yfiR-M2 mutant strains were crosslinked by addition of formaldehyde and YfiR-M2 detected by immunoblot analysis. 0 = sample before crosslinking; 20 = sample taken 20 min after formaldehyde addition; 20* = 20 min sample, boiled to break crosslinks. Black arrows indicate major bands corresponding in size to an YfiR-M2 monomer (20 kDa) and an YfiR-M2 oligomer (40 kDa), respectively. D) Bacterial two-hybrid analysis of YfiN and YfiR interactions. Positive interactions produce a red color on MacConkey indicator plates. Clockwise from top left, the cartoons denote YfiN-YfiN, YfiR-YfiR and HAMP domain-YfiN interactions. E) A model for YfiBNR function. YfiN is a membrane-localized DGC and is subject to product inhibition and control by YfiR. YfiB activates YfiN, possibly by releasing YfiR-mediated repression. OM and IM refer to the outer and inner membranes, respectively and PG refers to the peptidoglycan layer.