Abstract
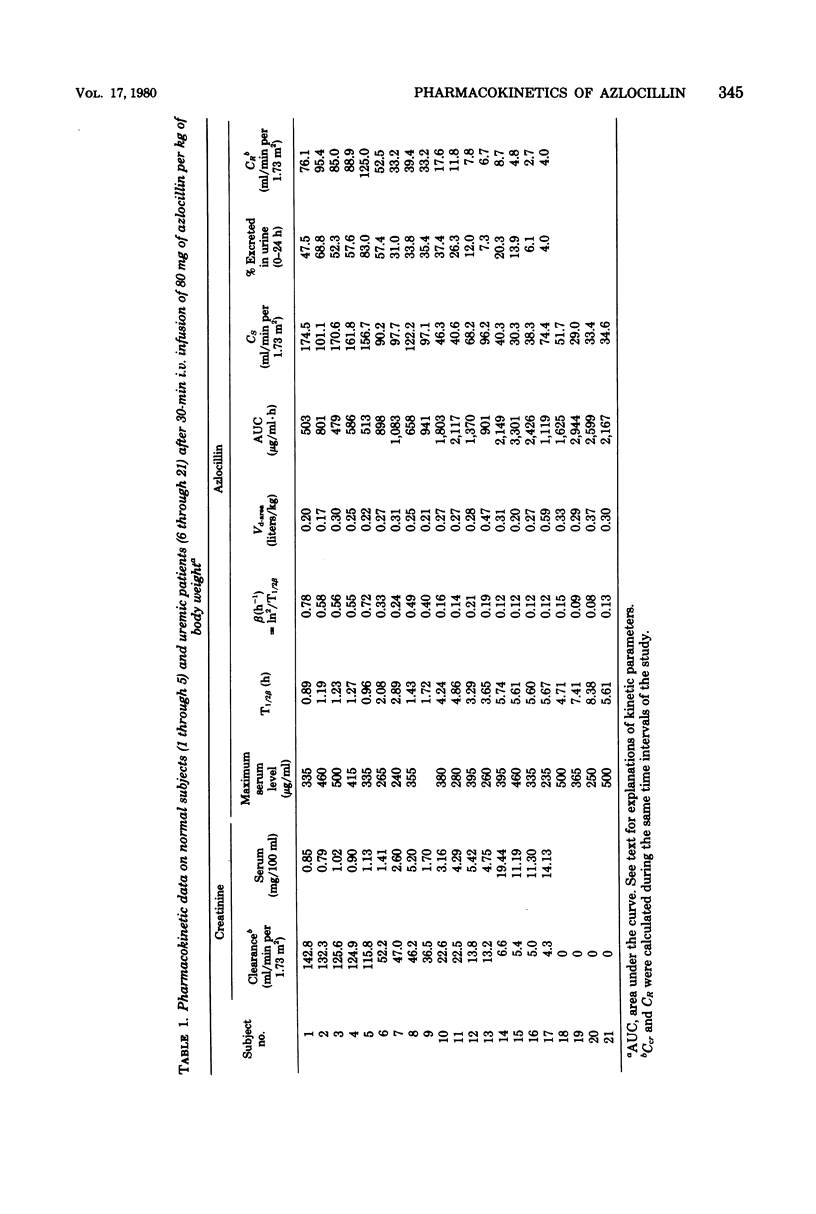
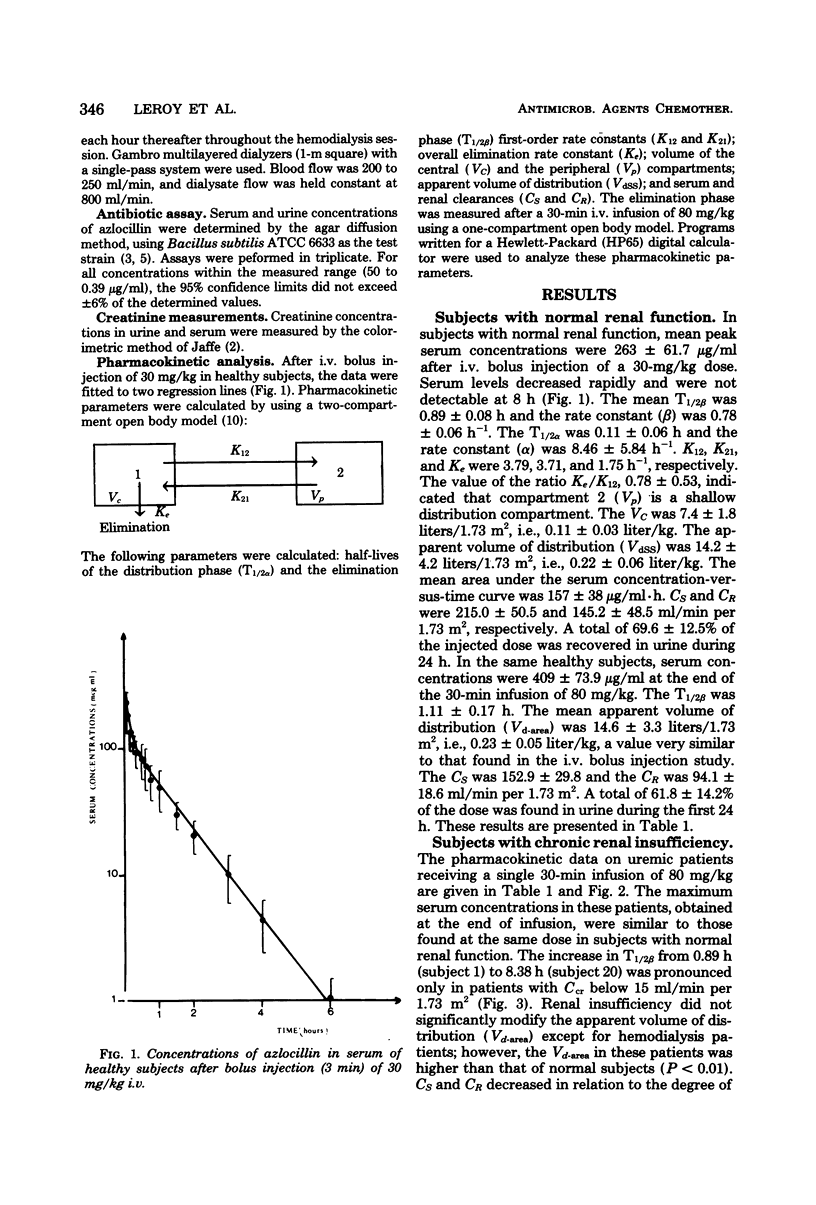
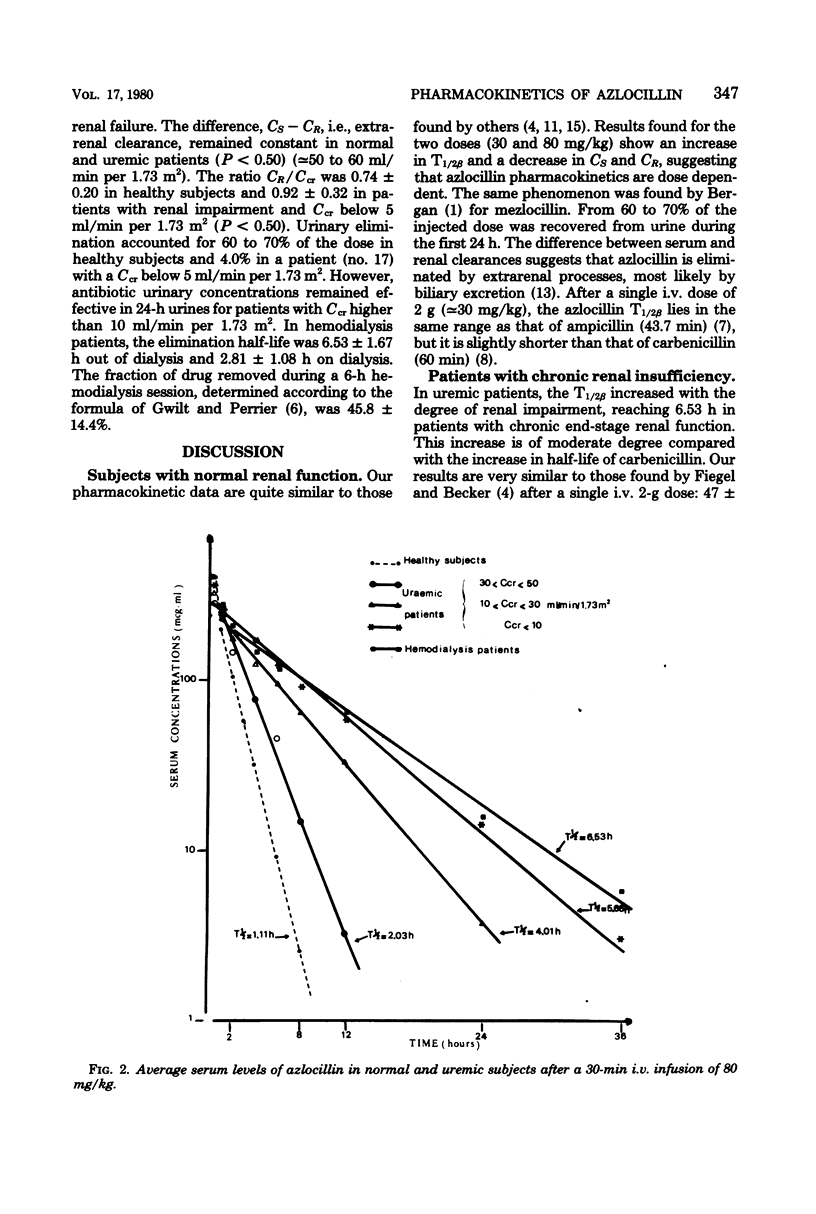
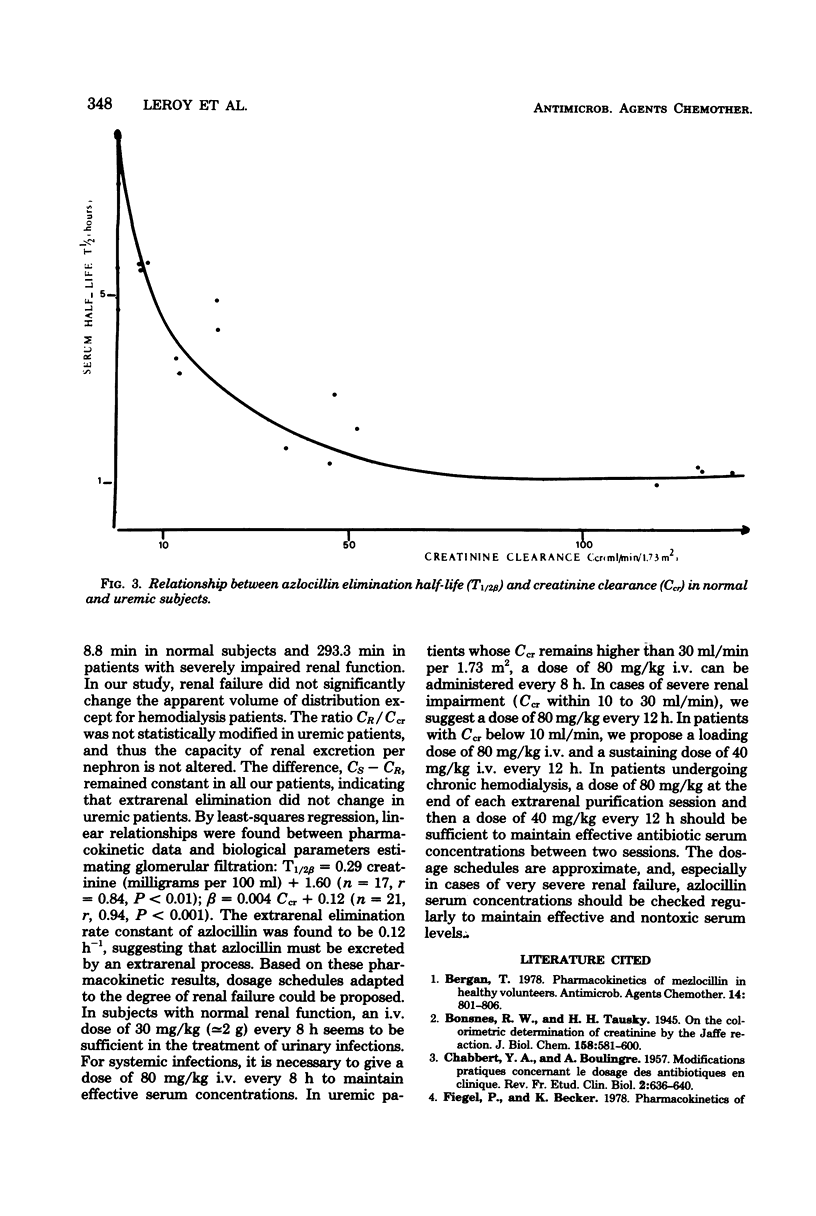
The pharmacokinetics of azlocillin were investigated in five healthy subjects and in 16 subjects with chronic renal failure. After intravenous bolus injection of a single dose of 30 mg/kg in normal subjects, pharmacokinetic data were calculated, using a two-compartment open body model. The mean distribution serum half-life (T1/2α) was 0.11 h, and the mean elimination serum half-life (T1/2β) was 0.89 h. The volume of the central compartment (VC) was 7.36 liters/1.73 m2, and the apparent volume of distribution (Vdss) was 14.15 liters/1.73 m2, i.e., 21.9% of body weight. The T1/2β after a 30-min intravenous infusion of 80 mg/kg to the same healthy subjects was 1.11 h. Serum clearances (CS) for the 30- and 80-mg/kg doses were 215.0 and 152.9 ml/min per 1.73 m2. The mean renal clearances (CR) were 145.2 and 94.1 ml/min per 1.73 m2 for the respective doses. Between 61.8 and 69.6% of the injected dose was recovered in urine during the first 24 h. The elimination half-life in subjects with chronic renal impairment increased with the degree of renal insufficiency. After a 30-min intravenous infusion of 80 mg/kg the T1/2β values were 2.03, 4.01, and 5.66 h with creatinine clearances (Ccr) within 30 to 50, 10 to 30, and <10 ml/min per 1.73 m2, respectively. Urinary elimination was inversely related to the degree of renal impairment. In four patients out of and on a 6-h hemodialysis session mean elimination half-life values were 6.53 and 2.81 h, respectively. The fraction of drug removed by dialysis was 45.8%. The linear relationships between the elimination of half-life (T1/2β) and serum creatinine and the elimination rate constant (β) and creatinine clearance (Ccr) provided a basis for adjustment of dosage in renal failure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergan T. Pharmacokinetics of mezlocillin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):801–806. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y., BOULINGRE H. Modifications pratiques concernant le dosage des antibiotiques en clinique. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1957 Jun;2(6):636–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiegel P., Becker K. Pharmacokinetics of azlocillin in persons with normal and impaired renal functions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):288–291. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwilt P. R., Perrier D. Plasma protein binding and distribution characteristics of drugs as indices of their hemodialyzability. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Aug;24(2):154–161. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978242154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman T. A., Cestero R., Bullock W. E. Pharmacodynamics of carbenicillin in hepatic and renal failure. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Aug;73(2):173–178. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-2-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Niestrath U., Koeppe P., Langmaack H. Azlocillin und Mezlocillin: Zwei neue semisynthetische Acylureidopenicilline. Infection. 1977;5(3):163–169. doi: 10.1007/BF01639753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D., Bodey G. P. Azlocillin: in vitro studies of a new semisynthetic penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):865–870. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Krassemann C., Ungerechts J., Schmitz H. J. Die in-vitro-Aktivität von Mezlocillin, Azlocillin und Carbenicillin gegen Bacteroidaceae unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Fragilis-Gruppe. Infection. 1977;5(1):17–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01639104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Schomerus M., Hengstmann J. H. Zur Pharmakokinetik von Azlocillin, einem neuen halbsynthetischen Breitspektrumantibiotikum. Infection. 1976;4(2):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01638344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


