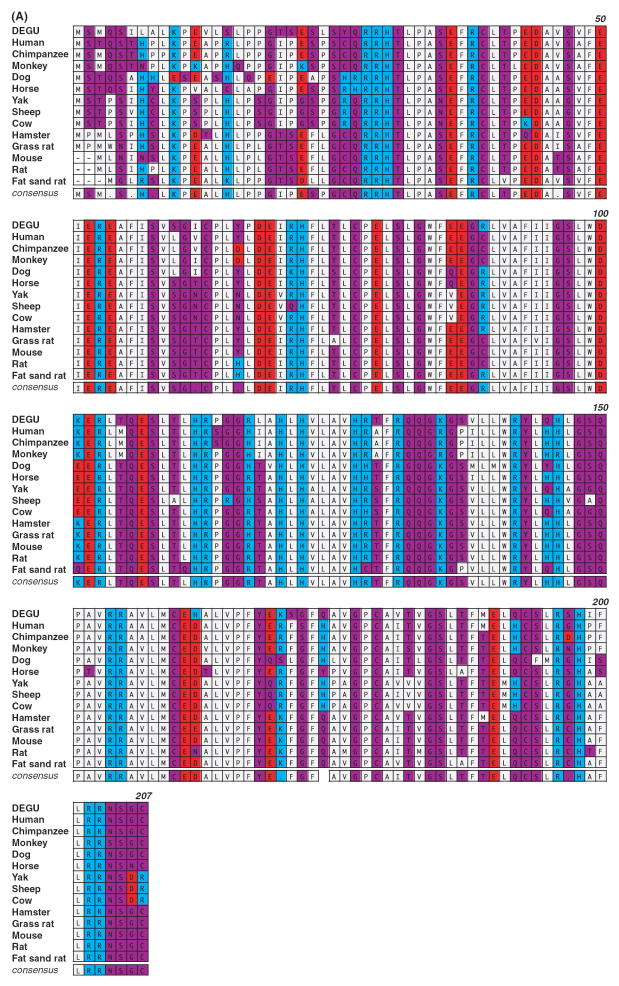
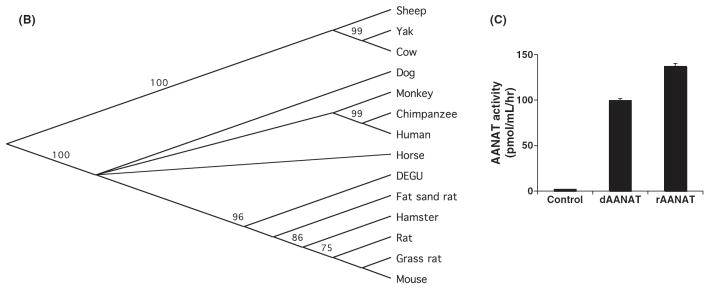
Fig. 2.
Degu Aanat cloning and analysis. (A) Amino acid sequence comparison of AANAT from degu and other mammalian species is shown. The sequence comparison was performed using MacVector ClustalW alignment program and was color-coded based on functionality of the amino acids. Acidic residues were marked in red, basic residues in blue, hydrophobic residues in gray, and hydrophilic residues in purple. The numbers indicated on the upper right lines denote the amino acid positions based on the degu AANAT sequence. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of degu AANAT. A diagram of the relationship between the degu AANAT amino acid sequences and AANATs from other mammalian species is shown. The phylogenic tree was constructed using the Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic mean (UPGMA) method. The confidence index assigned to particular nodes in the tree (numbers shown) was estimated using the bootstrap re-sampling approach with Poisson-correction. Compared with the other rodents, the degus AANAT appears to be more closely related to those of ungulates and primates. (C) Degu AANAT expression in HEK293 cells. Cells transfected with empty vector (control), degu Aanat cDNA (dAANAT), or rat Aanat cDNA (rAANAT) were incubated with 5-methoxytryptamine (final concentration at 1 uM) for 3.5 hr at 37°C. Supernatants were harvested and measured for melatonin production using HPLC. The results were confirmed in at least three independent experiments. The activity of the degu enzyme was comparable to the activity of rat AANAT enzyme expressed in HEK293 cells.