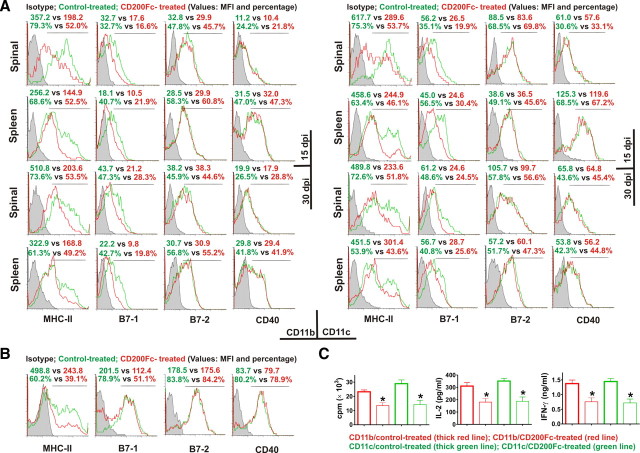
Figure 5.
CD200Fc inhibits antigen-presenting activity of microglia/macrophages and DCs. A, Immune cell populations were isolated from the spinal cords and spleens of control- and CD200Fc-treated mice on days 15 and 30. MHC-II, CD80 (B7-1), CD86 (B7-2), and CD40 expressions were analyzed by flow cytometry with gating on live CD11b+ or CD11c+ cells. Four to six mice per group with average clinical EAE were included, and data demonstrated are representative results. Histograms and quantifications on the same gating are shown. CD200Fc downregulated the expression of MHC-II and CD80 (B7-1), but not CD86 (B7-2) or CD40, in CD11b+ and CD11c+ cells. B, Primary cultures of microglia were stimulated in vitro with 10 ng/ml IFN-γ (for MHC-II) or 0.1 μg/ml LPS (for CD80, CD86, and CD40) in the presence of 100 μg/ml control IgG2a or CD200Fc. Cells were collected at 48 h, and the expressions of MHC-II, CD80, CD86, and CD40 were analyzed by flow cytometry. Similar effects of CD200Fc as in vivo were observed. Data demonstrated are representative of four independent experiments. Histograms and quantifications on the same gating are shown. C, CD11b+ and CD11c+ cells were isolated using fluorescence sorting from the spinal cords of six control- and six CD200Fc-treated mice, respectively, with average clinical EAE on day 20. The cells were used as APCs in vitro to stimulate cultured 2D2 mouse T cells in the presence of 100 μm MOG. At 48 h, cell proliferation was measured by [3H]thymidine incorporation. IL-2 and IFN-γ production was determined by Luminex assays. *p < 0.01 versus controls. MFI, Mean fluorescence intensity.