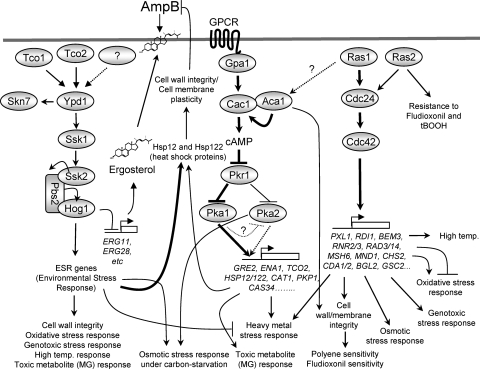
Fig. 9.
Proposed model for the regulatory mechanisms of the Ras and cAMP signaling pathways in stress response and antifungal drug susceptibility in C. neoformans. The Ras1-dependent signaling pathway promotes cell survival under diverse environmental stresses, such as cell wall destabilization, osmotic shock, oxidative and genotoxic stresses, and high temperature, in a manner mediated by Cdc24 and Cdc42. Ras1 appears to affect resistance to antifungal drugs by maintaining cell wall and membrane integrity. Along with Ras1, Ras2 plays some minor role in controlling antifungal and oxidative stress sensitivity. The cAMP signaling pathway is involved in responses to stress from heavy metals and toxic metabolites. Notably, small heat shock proteins, Hsp12 and Hsp122, are positively regulated by the cAMP signaling pathway and appears to affect resistance against AmpB treatment. However, expression of HSP12 and HSP122 is much more significantly regulated by the HOG pathway.