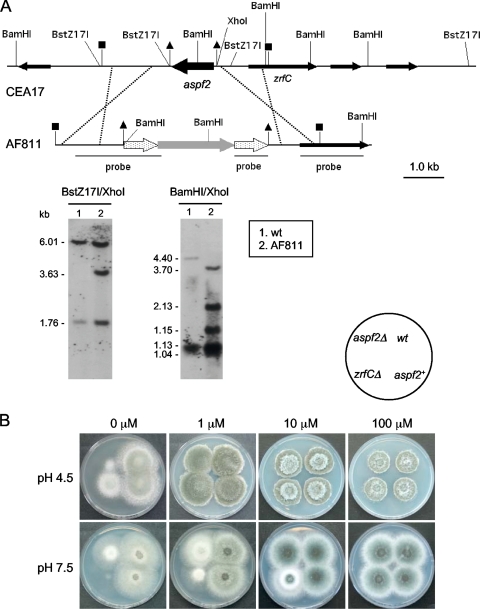
Fig. 8.
Construction and phenotypic analysis of aspf2Δ strains. (A) A 1.2-kb BstZ17I-XhoI DNA genomic fragment containing the complete coding sequence of aspf2 in CEA17 (delimited with triangles) was replaced by the lacI-pyrG-lacI cassette (gray arrow flanked by dotted arrows) in the aspf2Δ (AF811) strain by the use of a 6.65-kb DNA fragment obtained from plasmid pASPF25 as transforming DNA. All strains harbored the correct integration event at the aspf2 locus, as verified by Southern blotting using as a probe a mixture of a DNA fragment obtained by PCR with the oligonucleotide pair JA187 and JA26 and plasmid pASPF25 as the template and a SmaI-BglII fragment obtained from plasmid pZRF39. Only relevant restriction sites are indicated. The source of the genomic DNA, the restriction enzymes used in the digestions, and the sizes of the fragments detected that match the expected sizes are specifically indicated in each panel. (B) Growth of A. fumigatus strains AF811 (aspf2Δ), AF881 (aspf2+), and AF431 (zrfCΔ) on both acid (SDAE; pH 4.5) and alkaline (SDNE; pH 7.5) zinc-limiting agar media not supplemented with Zn2+ or supplemented with 1 to 100 μM Zn2+, as indicated at the top of each panel.