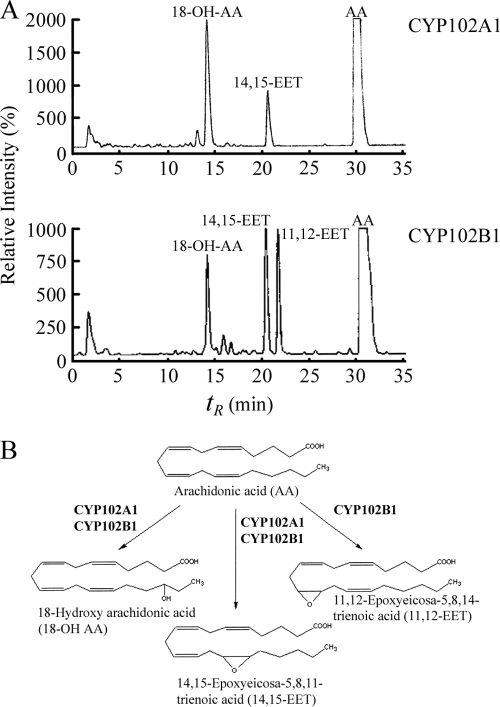
FIG. 2.
Arachidonic acid hydroxylation by CYP102A1 and CYP102B1 in heterologous electron transfer systems. (A) The positions of arachidonic acid and major products are shown in each case as indicated. The concentrations of the individual protein components used were 1 μM CYP102A1 and 1 μM CYP102B1, 1.0 μM spinach ferredoxin reductase, and 1.6 μM spinach ferredoxin. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and in all control experiments (without CYP or without reductase), no product formation was observed (data not shown). (B) Metabolic pathways for the catalysis of arachidonic acid by CYP102A1 and CYP102B1.