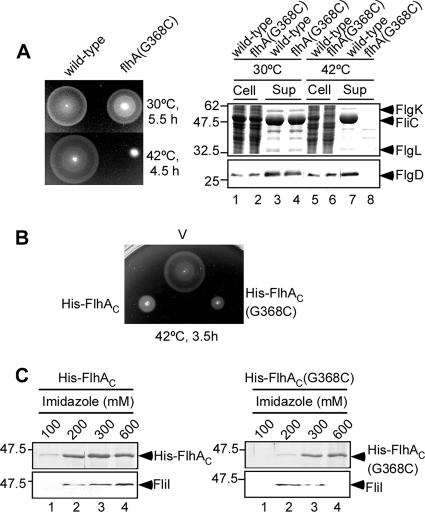
FIG. 1.
Characterization of the temperature-sensitive flhA(G368C) mutant. (A) (Left panel) Swarming motility of SJW1103 (wild type) and SJW2228 [flhA(G368C)] on soft agar plates at 30°C and 42°C. (Right panel) Secretion assays. Secretion of FliC, FlgK, and FlgL was analyzed by Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining (upper panel). Secretion of FlgD was measured by immunoblotting with a polyclonal anti-FlgD antibody (lower panel). Cell, whole-cell proteins; Sup, culture supernatant fractions. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left. (B) Dominant negative effect on wild-type swarming motility of SJW1103 transformed with pTrc99A (V), pMM102 (His-FlhAC) or pMM102(G368C) [His-FlhAC(G368C)] on soft agar plates containing 0.1 mM IPTG at 42°C. (C) Pull-down assay. The soluble fractions prepared from SJW1103 overproducing His-FlhAC (left panel) or His-FlhAC(G368C) (right panel) were loaded onto an Ni-NTA agarose column. After washing, proteins were eluted with a buffer containing 100 mM, 200 mM, 300 mM, and 600 mM imidazole. Pull-down assays were done at 42°C. Eluted His-FlhAC was analyzed by CBB staining, while eluted FliI was detected by immunoblotting with a polyclonal anti-FliI antibody.