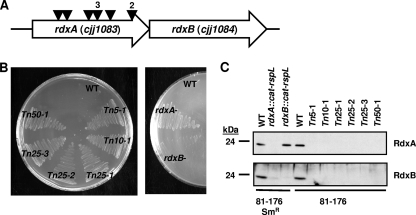
FIG. 1.
Mtzs and Mtzr phenotypes and production of RdxA and RdxB in C. jejuni transposon and site-directed mutants. (A) Identification of Mtzr darkhelmet transposon mutants of C. jejuni 81-176. Triangles represent locations of the darkhelmet transposons within rdxA. Numbers above triangles indicate the numbers of mutants identified with transposon insertions at identical locations, suggesting that these mutants were likely siblings. (B) Mtzs and Mtzr phenotypes of wild-type C. jejuni 81-176 (WT), isogenic darkhelmet transposon mutant strains (left), and wild-type 81-176 Smr (WT) and isogenic site-directed mutant strains (right) after 48 h of growth on MH agar containing 10 μg ml−1 Mtz. (C) Immunoblot analysis of RdxA and RdxB production in whole-cell lysates of wild-type C. jejuni 81-176 or 81-176 Smr strains and derived transposon or site-directed mutants. For panels B and C, strains include wild-type DRH212 (81-176 Smr; WT producing RdxA and RdxB), DAR521 (81-176 Smr rdxA::cat-rpsL, which produces neither RdxA nor RdxB), DAR562 (81-176 Smr rdxB::cat-rpsL, which produces only RdxA), and wild-type 81-176 (WT).