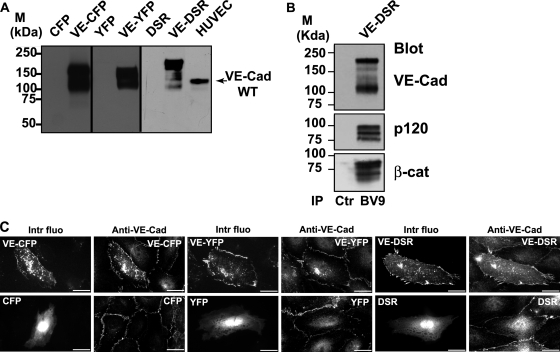
FIG. 2.
Characterization of the fluorescent proteins VE-CFP, VE-YFP, and VE-DSR. (A) Biochemical characterization of VE-CFP, VE-YFP, and VE-DSR. cDNA constructs expressing CFP, VE-CFP, YFP, VE-YFP, DSR, and VE-DSR were transfected in CHO cells. At 24 h posttranfection, lysates of these transfected cells were analyzed by Western blotting. The anti-VE-Cad MAb BV9 identified polypeptide bands of 165, 150, and 190 kDa corresponding to the expected sizes for VE-CFP, VE-YFP and VE-DSR, respectively. These bands were not detected in lysates of CHO cells expressing CFP, YFP, and DSR. In HUVECs used as a control, the wild-type (WT) form of VE-Cad was detected as a 135-kDa polypeptide band. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of VE-DSR with catenins. Anti-VE-Cad immunoprecipitation (IP BV9) was performed on VE-DSR-expressing CHO cells prior to being resolved on a 4 to 12% gradient gel, electrotransferred, and probed successively for VE-Cad, p120, and β-catenin (β-cat). As control, an immunoprecipitation performed on VE-DSR-expressing CHO cells using rabbit nonimmune IgG (Ctr) was analyzed in parallel. Molecular mass markers (M) are given at the margin of the panel. (C) Localization at cell-cell contacts of exogenous VE-CFP, VE-YFP, and VE-DSR transiently expressed in HUVECs. HUVECs expressing VE-CFP, CFP, VE-YFP, YFP, VE-DSR, and DSR were immunofluorescently stained for VE-Cad and observed by confocal microscopy. Then, the intrinsic fluorescence of the CFP, YFP, and DSR tags (Intr fluo) was compared to the immunofluorescent staining (Anti-VE-Cad). As expected, the three fluorescent VE-Cad proteins were mainly expressed at cell-cell junctions and on filopodia recapitulating the staining pattern of endogenous VE-Cad. In contrast, the proteins CFP, YFP, and DSR did not present a specific localization. Bars, 20 μm.