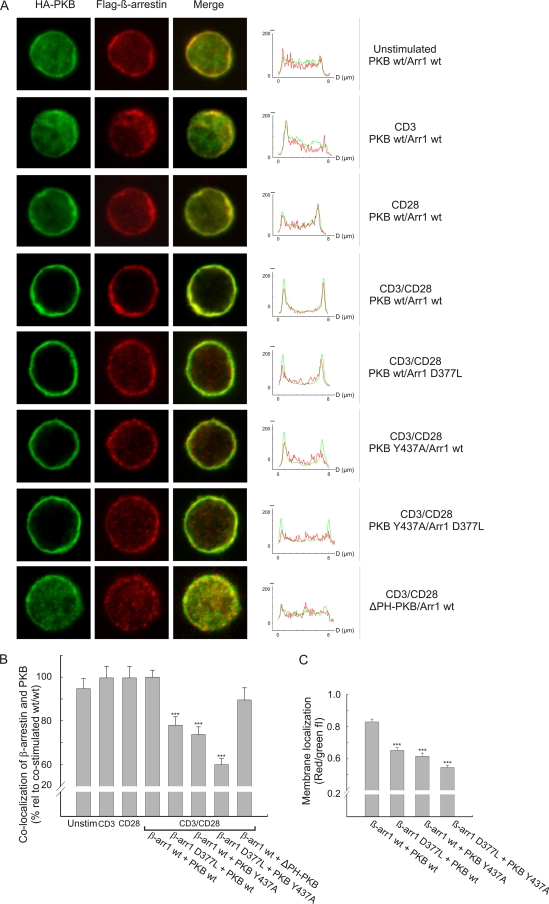
FIG. 4.
Recruitment of the β-arrestin/PKB complex depends on the PKB PH domain. (A) Human primary T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged β-arrestin 1 and HA-tagged PKBα constructs as indicated, and the cells were stimulated with anti-CD3, anti-CD28, or a combination of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 2 min, followed by cross-ligation with F(ab′)2-fragments for 3 min as indicated. PKBα was visualized using an Alexa488-conjugated HA-antibody (green), whereas β-arrestin was visualized using an anti-Flag antibody followed by staining with an isotype-specific Alexa546-conjugated secondary antibody (red). In the right panels, z-line scans of the immunofluorescence images show the green and red fluorescence intensity profiles. wt, wild type. (B) Colocalization of β-arrestin and PKB was calculated by quantifying the number of pixels that were both green and red positive throughout the cell. The data are presented as means ± SEM, and 30 to 35 images per group were analyzed. ***, P < 0.001. (C) Membrane localization was measured as red (arrestin)/green (PKB) fluorescence intensity, and this ratio was determined by calculating the areas below the red and green fluorescence intensity profiles, respectively. For each cell image, two z-line scans were performed and four membrane regions examined. The diameter of each region was set to 1 μm, and 10 images per group were analyzed. The data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 40). ***, P < 0.001.