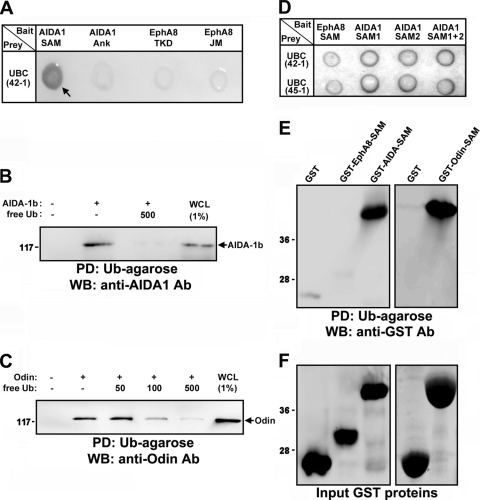
FIG. 1.
Yeast two-hybrid screening showing that ubiquitin interacts with AIDA1-SAM domains. (A) Analysis of the binding of AIDA1-SAM domains to ubiquitin by X-Gal staining. As negative controls, the ankyrin (Ank) repeats of AIDA-1b, the tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) of EphA8, and the JM domain of EphA8 served as bait. UBC42-1 is a clone identified through library screening that contained part of human ubiquitin chain gene (UBC). (B) Pulldown (PD) assay using Ub-agarose beads to probe lysates of HEK293 cells expressing full-length AIDA-1b. Free ubiquitin (500 nM) was used as a competitor for binding to Ub-agarose. WB analysis was carried out to determine the level of AIDA1 bound to Ub-agarose. Ab, antibody. (C) Experiments were performed as described for panel B, except that cell lysates from Odin-expressing cells were used. WCL, whole-cell lysate. (D) A yeast two-hybrid assay was performed as described for panel A. SAM1 and SAM2 indicate the isolated SAM domains of AIDA-1. UBC45-1 represents a second UBC clone identified through library screening. (E) Ub-agarose pulldown assay of SAM domains fused to GST. (F) The samples from panel E were examined by Coomassie blue staining to determine the levels of GST fusion protein.