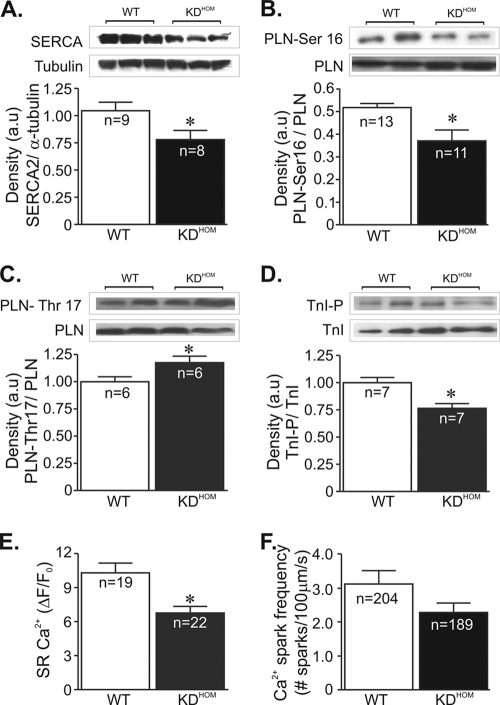
FIG. 4.
Ca2+ signaling components in VAChT KDHOM hearts. In panels A to D, the top image is a representative Western blot and the bottom shows an average densitometry graph (n, number of heart samples analyzed). (A) SERCA2 levels in VAChT KDHOM hearts were observed to be significantly reduced compared to levels in WT hearts. Phosphorylated-PLN levels at the protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent site (Ser-16) were lower in VAChT mutant hearts (B), while phospho-Thr-17-PLN levels were increased in these hearts (C). (D) Phospho-Ser-23/24-troponin I levels were decreased in VAChT mutant hearts relative to WT hearts. Tubulin expression levels were used as a loading control. (E) The SR Ca2+ content in ventricular cardiomyocytes from VAChT mutants was significantly reduced compared to that in WT cells. n, number of cells. (F) Ca2+ spark frequency showed a tendency to be lower in VAChT KDHOM cardiomyocytes than in WT mice, but the difference was not statistically different. n, number of cells. *, P < 0.05.